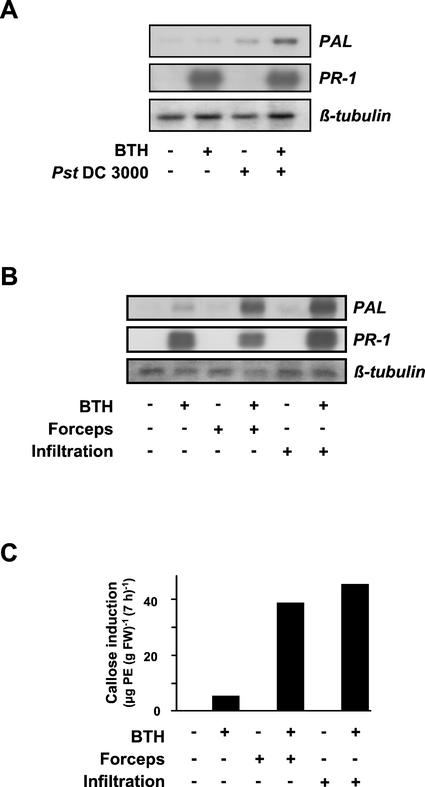
Figure 1.
Effect of priming by BTH on PAL and PR-1 gene activation and callose induction. Arabidopsis plants were sprayed with 100 μm BTH (+) in a wettable powder carrier or with the wettable powder carrier only (−). Three days later, leaves of the plants were left untreated (−), wounded with forceps (B and C; +), infiltrated with water (B and C; +), or inoculated with Pst DC3000 (A; +). Mock inoculations were performed by dipping plants into MgCl2/Silwet in the absence of bacteria (A; −). A and B, Total RNA was extracted from an aliquot of leaves 4 h (A) or 2 h (B) after treatment and assayed for accumulation of PAL mRNA by RNA gel-blot analysis. Another aliquot of leaves was harvested at the 24-h time point post-treatment and was analyzed for the accumulation of PR-1 transcripts (A and B). To document equal sample loading and transfer of RNA, the membranes from the PAL blots were stripped and reprobed with a 32P-labeled Arabidopsis β-tubulin cDNA. C, At the 7-h time point after wounding or infiltration of water, callose was extracted and determined from yet another aliquot of leaves. At this time point, leaves treated with the wettable powder carrier only contained 45.4 μg of pachyman equivalents (PE; g fresh weight)−1 background callose level, which supposedly is due to the high callose content observed in the leaf trichomes of Arabidopsis (A. Kohler, S. Schwindling, and U. Conrath, unpublished data). This value was subtracted from all samples. Values given are averages of two replicates. For variations in callose values obtained by the extraction method used, see Kohler et al., 2000. The establishment of SAR in the BTH-sprayed plants was confirmed in a parallel assay in which two upper leaves of four plants treated with wettable powder or BTH for 3 d were dip-inoculated with a suspension of Pst DC3000 (35 × 106 cfu mL−1). Three days later, those plants that had been pretreated with the wettable powder carrier were diseased and exhibited wet chlorotic lesions, whereas the BTH-pretreated plants remained free of visible symptoms (data not shown).