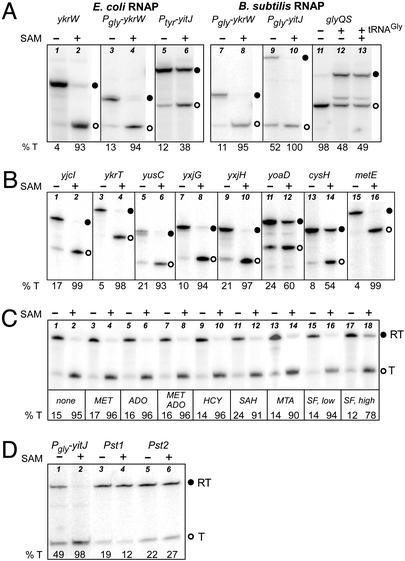
Figure 2.
In vitro transcription of S box genes. ○, Terminated transcript; ●, read-through transcript. Percent termination (% T) is shown at the bottom of each lane. (A) SAM-dependent transcription termination. DNA templates were transcribed with E. coli (lanes 1–6) or B. subtilis (lanes 7–13) RNAP. Lanes 1 and 2, ykrW DNA; lanes 3, 4, 7, and 8, Pgly-ykrW DNA; lanes 5 and 6, Ptyr-yitJ DNA; lanes 9 and 10, Pgly-yitJ DNA; lanes 11–13, glyQS DNA. SAM was added at 150 μM where indicated (lanes 2, 4, 6, 8, 10, and 13). tRNAGly was added at 70 nM for lanes 12 and 13. The Pgly-yitJ constructs contain additional sequences downstream of the terminator, resulting in a larger read-through product than is observed with Ptyr-yitJ DNA. (B) SAM-dependent transcription termination of multiple B. subtilis S box leaders. DNA templates were transcribed with B. subtilis RNAP in the presence (lanes 2, 4, 6, 8, 10, 12, 14, and 16) or absence (lanes 1, 3, 5, 7, 9, 11, 13, and 15) of SAM (150 μM). Gene names are shown above each pair of lanes. (C) Specificity of SAM-dependent transcription termination of the B. subtilis ykrW leader. The ability of SAM-related compounds to stimulate termination by E. coli RNAP, and to block SAM-dependent termination, was tested. MET, methionine; ADO, adenosine; HCY, homocysteine; MTA, methylthioadenosine; SF, sinefungin. All compounds were tested at 1.5 mM except homocysteine (500 μM) and sinefungin, which was tested at both 500 μM (low, lanes 15 and 16) and 1.5 mM (high, lanes 17 and 18). SAM was included at 7.5 μM where indicated. (D) Effect of yitJ leader mutations on SAM-dependent transcription termination. DNA templates were Pgly-yitJ constructs; mutations are shown in Fig. 1. Transcription was with E. coli RNAP, in the presence (lanes 2, 4, and 6) or absence (lanes 1, 3, and 5) of SAM (150 μM). Templates were yitJ (lanes 1 and 2), yitJ-Pst-1 (lanes 3 and 4), and yitJ-Pst-2 (lanes 5 and 6).