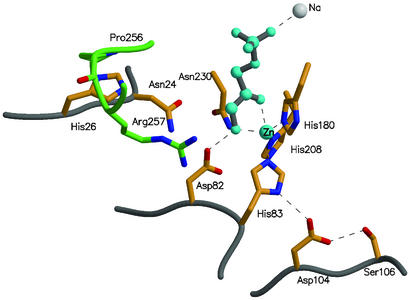
Figure 5.
The active site of the wild-type class II TBP aldolase (AgaY). The locations of a number of active site residues and the positions of the residues mutated during the evolution of the new enzyme are shown. Asp-104 and Ser-106 form a hydrogen bond network with His-83 (one of the ligands to the catalytic zinc cation) and through this to the substrate analogue, phosphoglycolohydroxamate (cyan), and Asp-82, the residue responsible for protonation at C4 (32). Changes in this network are likely to produce subtle changes in the orientation of the two substrates, leading to altered stereochemistry of bond formation. His-26 lies between the active site and the α-10 to α-11 loop of the adjacent subunit (residues 255–258 of this loop are shown in green). This loop contains Pro-256 and contributes Arg-257, responsible for binding the C6 phosphate of the substrate. The changes found during evolution of altered stereochemistry (P256L and H26Y) are likely to cause subtle repositioning of Arg-257 and hence the G3P end of the substrate to result in the stereochemical changes observed. The coordinates are taken from Protein Data Bank (PDB ID code 1GVF) (32) and the figure was made by using MOLSCRIPT (34) and RASTER3D (35).