Figure 1.
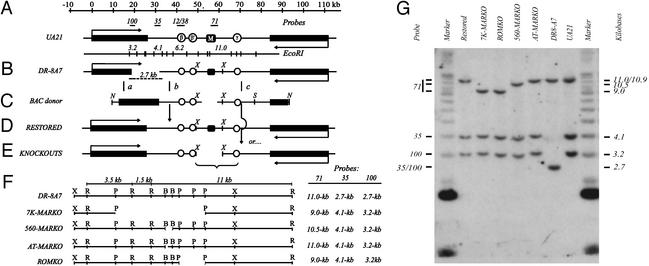
The DHFR locus and the ROKO approach. (A) The 120-kb region encompassing the DHFR and 2BE2121 (53, 54) genes in the WT hemizygote, UA21, showing the position of three preferred replication initiation sites (ori-β, ori-β′, and ori-γ; refs. 16, 17, and 21) and the intergenic MAR (black square; ref. 22). Positions of relevant hybridization probes and an EcoRI map of the region are shown above and below the map, respectively. (B) The DHFR-deficient variant, DR-8A7, with the diagnostic deletion junction EcoRI fragment shown below. (C) The BAC donor used to restore the DHFR gene and knock out the downstream sequence of interest, showing the XhoI fragment into which each deletion was engineered (in the example shown, a 7-kb region encompassing the MAR; see text). (D and E) Recombination near sites a and b (C) leads to a restored WT derivative (D), whereas recombination near sites a and c leads to restoration of the gene and simultaneous deletion of the downstream target (E). (F) Detailed maps showing positions of deletions (see text) and sizes of resulting diagnostic EcoRI fragments. X, XhoI; R, EcoRI; P, PstI; B, BstEII. (G) Southern analysis of EcoRI digests of each cell line, hybridized with a mixture of probes 100, 35, and 71 (see A and F). Size markers are a mixture of a 1-kb ladder and high molecular weight standard (Invitrogen).