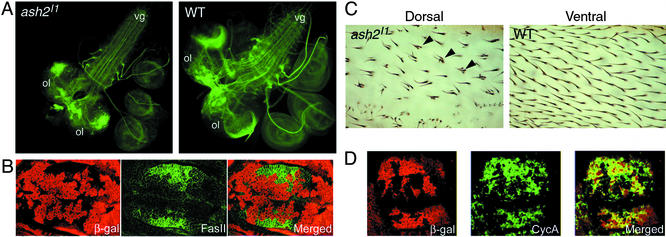
Figure 5.
ash2 has a role in regulating cell adhesion, development of neural system, and cell cycle. (A) Third instar larval brains from ash2I1/ash2I1 and WT individuals stained with anti-FASII. ol, optic lob; vg, ventral ganglion. Note the disruption of the neural pattern in both the optic lobe and the comissures of the ventral ganglion. (B) FLP-FRT clones on Minute (M−) background of ash2I1 mutant cells from a wing imaginal disc tested for the up-regulated protein Fasciclin II (green). (C) Detail of a clone ash2I1/ash2I1 in the dorsal layer of cells of an adult wing (Left) and the same area (WT tissue) focused on the opposite wing side (Right). Note that in the WT condition each cell develops one hair, whereas in the dorsal mutant surface some cells develop multiple hairs (arrowheads). (D) Immunodetection of the down-regulated CycA (green) on M− background FLP-FRT clones. (B and D Left) Staining with anti-β-galactosidase antibody in red (see Fig. 1 legend).