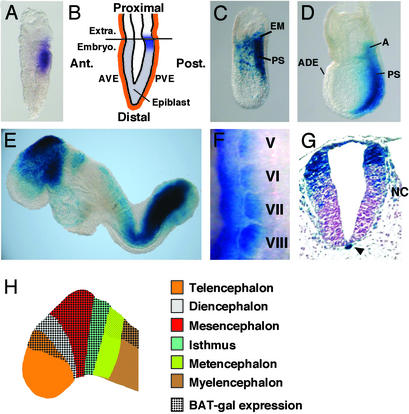
Figure 1.
BAT-gal expression during early development. (A) First expression in the posterior epiblast of prestreak stage embryo detected by in situ hybridization with antisense β-galactosidase probe. (B) Diagram indicating the location of lacZ-positive cells (in blue) at the prestreak stage. Ant., anterior; Post., posterior; Extra., extraembryonic region; Embryo., embryonic region; AVE, anterior visceral endoderm; PVE, posterior visceral endoderm. (C and D) Whole-mount X-Gal staining of embryos at early- and late-streak stage, respectively. A, allantois; ADE, anterior definitive endoderm; PS, primitive streak. (E) E8.5 embryo shows staining in the fore-, mid-, and hindbrain, tailbud, newly formed somites, and cardiac region. (F) Lateral view of lacZ in situ hybridization of 9.5-days postcoitum somites V–VIII (anterior is up and dorsal is left). Note the progressive restriction of BAT-gal staining in the dorsal medial portion of the dermomyotome. (G) Cross section through the caudal spinal cord. Arrowhead points to the notochord. Note the migrating neural crest cells (NC). (H) Diagram indicating the expression of BAT-gal in different regions of the brain at E8.5.