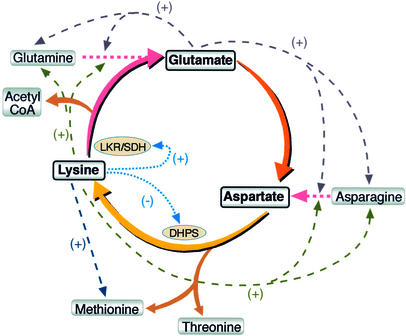
Figure 9.
Model Depicting Glu, Asp, and Lys at the Core of an Important Regulatory Loop in Plant Amino Acid Metabolism.
The hypothesized Glu-Asp-Lys metabolic loop is presented in the center, linked by orange, yellow, and pink arrows, respectively. A different branch of the Asp family pathway (brown arrows) synthesizes Thr and Met. The pathway of Lys catabolism produces acetyl-CoA (brown arrow). Two of the most important regulators in this loop are the extreme sensitivity of DHPS activity to feedback inhibition by Lys and the stimulation of LKR/SDH activity by excess Lys levels (light blue arrows) (for discussion, see Galili et al., 2001; Galili, 2002). Impairment of these two important regulatory elements causes extensive conversion of Glu and Asp to Lys, thereby activating several other metabolic regulatory circuits. We believe that the rapid reduction in Glu, an important regulatory amino acid, triggers increased synthesis of Gln and Asn and their conversion to Glu and Asp, respectively (dashed gray arrows). However, we cannot exclude the possibility that the increased Lys level triggers this metabolic change as well (dashed green arrows). In addition, the increased Lys level also triggers another novel regulatory circuit, resulting in a significant increase in Met level (dashed blue arrow). The significance of this novel regulatory circuit is unknown.