FIGURE 1. Determination of subunit composition and domain organization of M. tuberculosis acyl-CoA carboxylase.
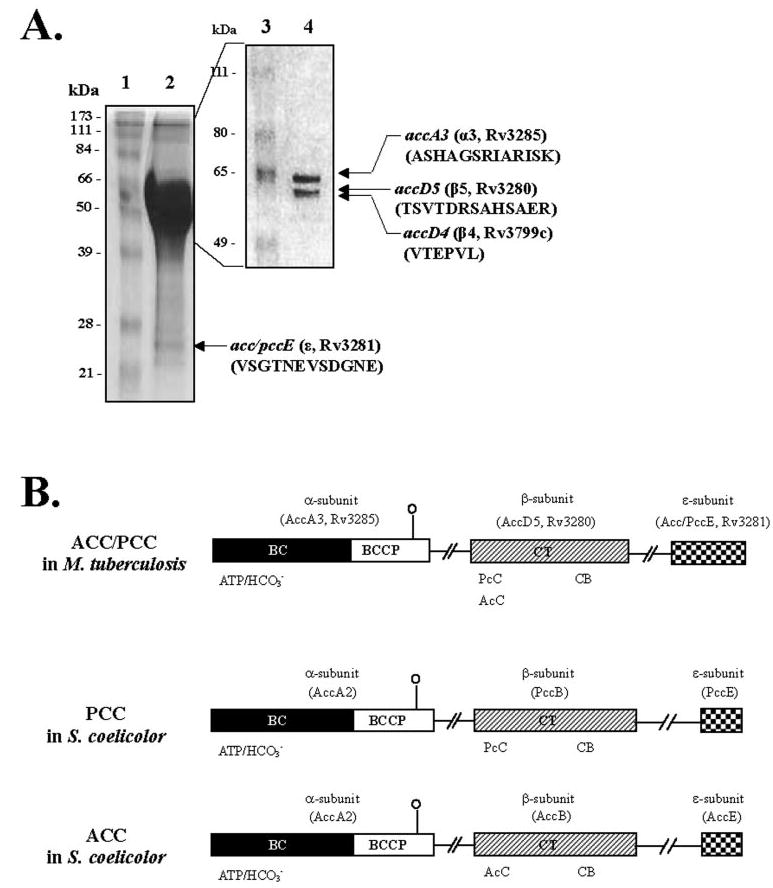
A, identification of the subunits of the biotin-dependent acyl-CoA carboxylase. Acyl-CoA carboxylase was purified by single-step avidin affinity chromatography, and the purified complex was resolved on 7.5% SDS-PAGE. The N-terminal amino acid sequences of the 63- (α3), 59- (β5), and 56- (β4) kDa bands were determined by Edman degradation. The 24-kDa band (ε) was resolved on 15% SDS-PAGE, and the amino acid sequence was determined by MALDI-TOF MS following tryptic digestion. Lane 1, molecular weight protein marker; lane 2, avidin-purified acyl-CoA carboxylase complex on 15% SDS-PAGE; lane 3, molecular weight protein marker; and lane4, 7.5% SDS-PAGE of avidin-purified acyl-CoA carboxylase. B, domain organization and amino acid sequence similarity of M. tuberculosis and S. coelicolor acyl-CoA carboxylase. Sequence similarities are shown by similarly shaded boxes. AccA3, Rv3285, acyl-CoA carboxylase α-subunit from M. tuberculosis; AccD5, Rv3280, propionyl-CoA carboxylase β-subunit from M. tuberculosis; Acc/PccE, Rv3281, acyl-CoA carboxylase ε-subunit from M. tuberculosis; AccA2, acyl-CoA carboxylase α-subunit from S. coelicolor; AccB, acetyl-CoA carboxylase β-subunit from S. coelicolor; PccB, propionyl-CoA carboxylase β-subunit from S. coelicolor; AccE, acetyl-CoA carboxylase ε-subunit from S. coelicolor; PccE, propionyl-CoA carboxylase ε-subunit from S. coelicolor; ATP/CO3−, biotin carboxylation domain that binds ATP and CO2 fixation, respectively; CB, putative carboxybiotin-binding domain; AcC and PcC, carboxyltransferase domain that binds acetyl-CoA and propionyl-CoA, respectively.
