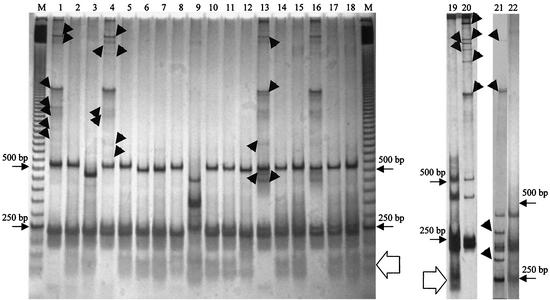
FIG. 1.
Identification of the homoduplex bands in the ITS homoduplex-heteroduplex polymorphism patterns separated in a MDE gel after mung bean nuclease digestion of the PCR products. Lanes M contain a 50-bp ladder. Normal ITS homoduplex-heteroduplex polymorphism profiles: lanes 1, 4, 13, 16, 20, and 21, B. weihenstephanensis 10204T, B. thuringiensis Ht39, B. anthracis 376, B. anthracis Cepanzo, B. anthracis Davis TE 702, and B. mycoides G2. ITS homoduplex-heteroduplex polymorphism profiles after treatment with mung bean nuclease: lanes 2 and 3, B. weihenstephanensis 10204T and B. pseudomycoides 617T; lanes 5 to 12, B. thuringiensis Ht39, B. thuringiensis 2046T, B. cereus V65SP, B. mycoides 2048T, B. mycoides G2, B. anthracis 256, B. anthracis 282, and B. cereus 31T; lanes 14 and 15, B. anthracis 376 and B. anthracis 779; lanes 17 and 18, B. anthracis Cepanzo and B. anthracis 663; lanes 19 and 22, B. anthracis Davis TE 702 and B. mycoides G2. The 250- and 500-bp bands of the ladder are indicated. Arrowheads indicate the heteroduplex products removed by the mung bean nuclease. The open arrows indicate degradation products of the heteroduplex bands.