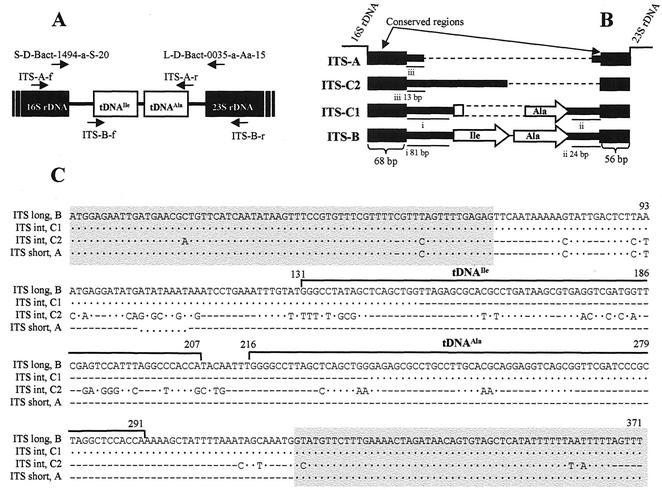
FIG. 2.
(A) Position of the tDNA-targeting primers designed for sequencing the long 16S-23S rDNA ITS of B. cereus group. S-D-Bact-1494-a-S-20 plus L-D-Bact-0035-a-A-15 (13) is the universal primer set initially used for ITS homoduplex-heteroduplex polymorphism analysis. ITS-A-f plus ITS-A-r and ITS-B-f plus ITS-B-r are primer sets used to amplify and sequence the 5′- and 3′-end regions, respectively, of the long ITS containing tRNA genes. (B) Schematic structure of the 16S-23S rDNA ITS types found in the B. cereus group. The genes encoding tRNA are indicated by open arrows. Conserved regions flanking 16S or 23S rDNA are indicated by bold bars. The other conserved regions are underlined and labeled i, ii, and iii. The broken lines are gaps for the alignment. (C) Sequence alignment of different types of 16S-23S rDNA ITS found in the B. cereus group. ITS B, long ITS of B. anthracis 7700; ITS C1, intermediate ITS of B. anthracis Davis TE702; ITS C2, intermediate ITS of B. mycoides G2; ITS A, short ITS of B. anthracis Cepanzo. Dots indicate nucleotides identical to those of ITS-B. Sequence gaps for the alignment are shown by hyphens. The genes encoding tRNA are indicated by a continuous black line. Conserved regions flanking 16S and 23S rDNA are shaded in grey.