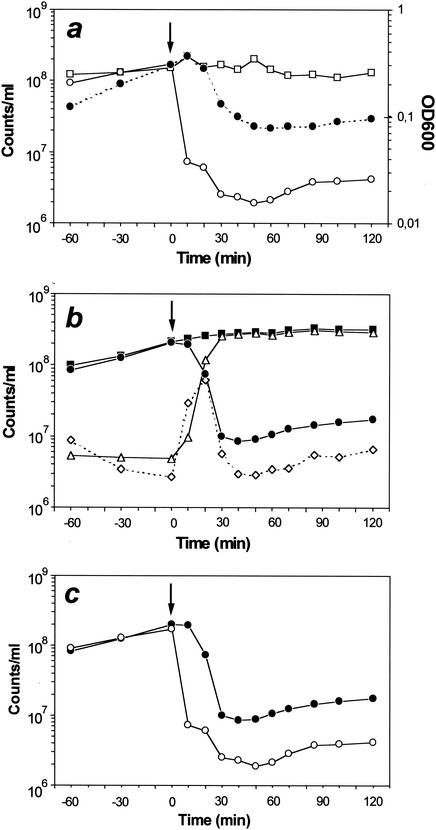
FIG. 5.
Comparison of quantitative analyses of ghost production by classical microbiological procedures (a) and flow cytometry (b). E. coli NM522(pML1) was grown at 28°C to mid-log phase and then shifted to 42°C for lysis induction at the time indicated by arrows. During the 3-h time course, OD600 (closed circles on dotted lines) was monitored and various samples were collected and analyzed to determine the total number of cells (□) and the number of reproductive bacteria (○) by classical procedures. Flow cytometric analysis included determination of the total number of cells (▪); the number of nonlysed and polarized (•) or nonlysed but depolarized cells (⋄); and the number of ghosts (▵). The data used to quantify the viable (reproductive or polarized) bacteria, derived from the classical or flow cytometric analyses, are presented separately (c). Bacterial numbers are shown as counts per milliliter. The sampling time points indicated refer to time points postinduction of lysis (0 min).