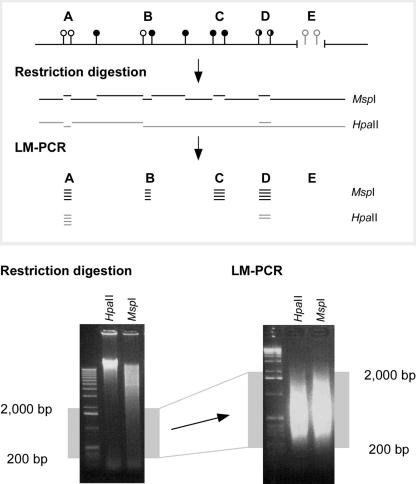
Figure 1.
Principle of the HELP assay. The HELP assay is based on a comparison of representations from the genome following digestion by HpaII or its methylation-insensitive isoschizomer MspI. The representations are limited to a size range of 200–2000 bp by the use of ligation-mediated PCR. The MspI representation is the total potential population of sites that could be generated by the HpaII representation were none of these sites to be methylated. However, as 55%–70% of these sites are methylated in animal genomes (Bird 1980; Bestor et al. 1984), the HpaII representation will always represent a subset of the MspI representation. By comparing the relative representation at individual loci, assignment can be made of cytosine methylation status. While loci such as A should be amplified in both the HpaII and MspI representations, the failure of HpaII to digest both sites at loci B and C will yield a representation from MspI alone, while the partial methylation depicted at locus D should generate a lower HpaII/MspI ratio than at locus A. If a locus is deleted (or has a sequence change at the enzyme cleavage sites) as shown at E, neither representation will generate the locus.