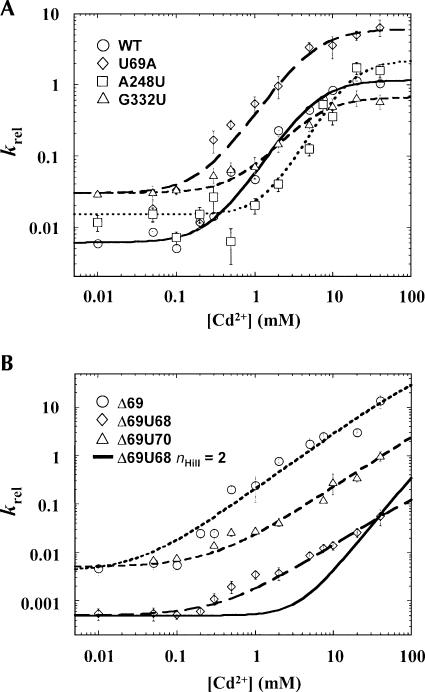
FIGURE 2.
Quantitative phosphorothioate rescue analysis of the effects of mutations in the P RNA catalytic core. (A) Cd2+ concentration dependence of k rel (k sulfur/k oxygen) for cleavage of pre-tRNAASP with a cleavage site RP phosporothioate modification by native P RNA (circle), and mutants A248U (square), G332U (triangle), and U69A (diamond) plotted as a function of a nonlinear form of the Hill equation as described previously (Shan et al. 2001). The effect of Cd2+ on rate is expressed as the ratio of the observed reaction rate for the phosphorothioate substituted substrate to the corresponding unmodified control (k rel), which controls for nonspecific effects of Cd2+ binding on the reaction. (B) Cd2+ concentration dependence of k rel for cleavage of the Rp phosporothioate-modified substrate by the Δ69 (circle), Δ69U68 (diamond), and Δ69U70 (triangle) mutant RNase P ribozymes. Solid black line reflects a plot of the data from Δ69U68 RNase P RNA plotted with n Hill fixed at 2. Note that all reactions were carried out in a constant background of 10 mM MgCl2 to ensure RNA folding and that there was essentially no inhibition of the observed reaction rate due to the presence of Cd2+ even at the highest concentrations tested (40 mM).