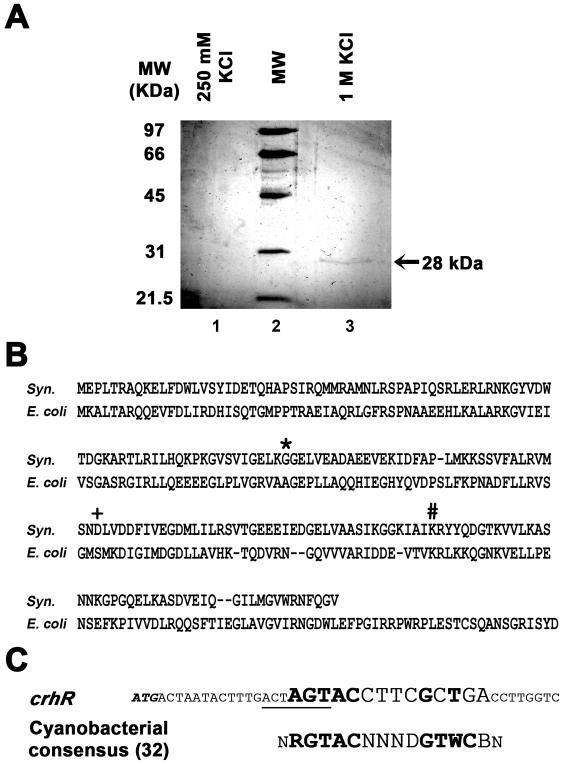
Figure 2.
Isolation and characterization of a crhR regulatory protein by affinity chromatography and LC/MS/MS. (A) A 28 kDa polypeptide interacts with the crhR ORF. A single polypeptide was isolated by DNA affinity chromatography using KC+5 as the target. Non-specifically bound proteins were removed by increasing KCl washes. Silver staining of eluted proteins separated by a 10% SDS–PAGE reveals a single polypeptide in the 1 M KCl elution. LC/MS/MS identified this polypeptide as the Synechocystis gene annotated as encoding LexA. Lane 1, 250 mM KCl wash; lane 2, low molecular weight standards (BioRad); lane 3, 1 M KCl wash. (B) Amino acid sequence analysis of the Synechocystis (gray) and E.coli (black) LexA proteins. Residues essential for E.coli LexA self-cleavage in response to DNA damage are indicated as follows: * = Ala-Gly self-cleavage site; + = Ser and # = Lys indicate the Ser-Lys dyad active site. (C) Alignment of the putative LexA binding region of the crhR gene (SpeI site is underlined) with the consensus cyanobacterial LexA binding sequence (32). Conserved residues are bolded. The LexA binding sequence within the crhR matches at 7 of 9 conserved residues with appropriate spacing.