Figure 2.
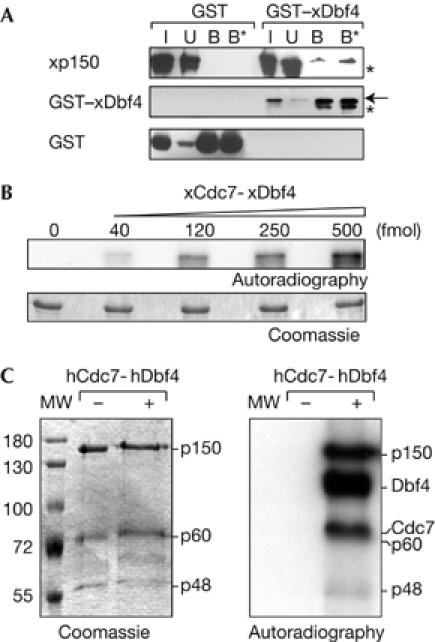
p150 interacts with and is phosphorylated by Cdc7-Dbf4 kinase in vitro. (A) Extract from bacteria coexpressing His6–xp150 with GST–xDbf4 or GST (used as control) was mixed with glutathione resin and pulled-down proteins were analysed by western blot. xp150, GST–xDbf4 and GST in the input (I, 10%), unbound (U) and bound fractions (B and B*, 0.5 and 1 M NaCl washes, respectively) are shown. The arrow indicates the position of full-length GST–xDbf4 and asterisks indicate degradation products. (B) Purified recombinant p150 was phosphorylated with ATPγ32P and increasing amounts of xCdc7-xDbf4 (in fmol) and resolved by SDS–PAGE. Coomassie-stained gel and its autoradiography are shown. (C) The whole CAF1 complex containing the three p150, p60 and p48 subunits was incubated with ATPγ32P without (−) or with (+) hCdc7-hDbf4 and resolved by SDS–PAGE. Coomassie-stained gel and its autoradiography are shown. Molecular weight (MW) markers and migration position of the CAF1 subunits, phosphorylated Dbf4 and Cdc7 are indicated. CAF1, chromatin assembly factor 1; Cdc7, cell division cycle 7 (hCdc7, human Cdc7; xCdc7, Xenopus Cdc7); Dbf4, Dumb bell former 4 (hDbf4, human Dbf4; xDbf4, Xenopus Dbf4); GST, glutathione S-transferase; SDS–PAGE, SDS–polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis.
