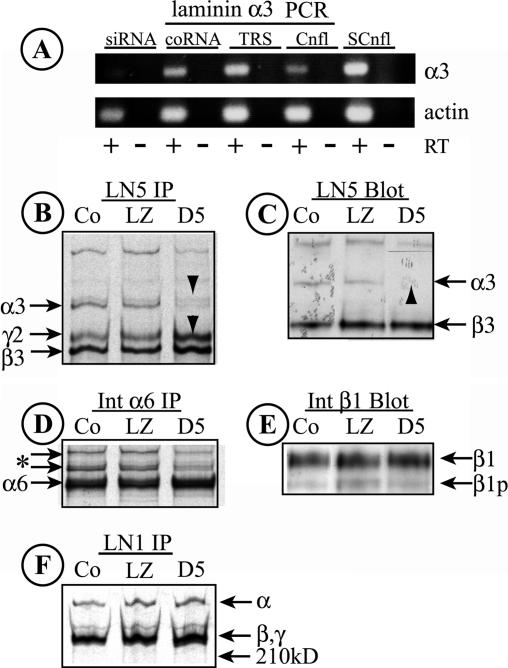
Figure 5.
Knockdown of laminin α3 with siRNA. (A) RNA was harvested from MDCK cells transfected for 2 d with either a synthetic RNA duplex specific for a target sequence in canine laminin α3 (siRNA), a control duplex not representing any known gene (coRNA), or transfection reagent alone (TRS). RNA was also harvested from confluent (Cnfl) or subconfluent (SCnfl) MDCK cell cultures. Laminin α3 and actin transcripts were detected by RT-PCR. RT, reverse transcriptase added to the reaction. Note the absence of a laminin α3 band with transfected siRNA. (B) LN5 was immunoprecipitated from detergent extracts of metabolically labeled control MDCK cells (Co) or cells infected with siRNA-expressing adenovirus (D5) or a control virus (LZ). In both Co and LZ samples, all three LN5 bands are visible; in the D5 siRNA sample, little laminin α3 can be seen, whereas the levels of laminin β3 and γ2 chains are increased (arrowheads). (C) Extracts from control (Co), Ad-LacZ–infected, and Ad-D5–infected MDCK cells were immunoblotted with anti-LN5. Laminin α3, which is weakly detected by the antibody, is absent in cells expressing siRNA (arrowhead). The laminin γ2 chain is not detected by the antibody. (D and F) The labeled cell extracts used to immunoprecipitate LN5 in B were sequentially immunoprecipitated with anti-α6 integrin (D) and anti-LN1 (F). No significant differences between the samples are evident, suggesting that siRNA-mediated knockdown of laminin α3 is specific. The two bands in D running more slowly than α6 (* and arrows) are unidentified but may correspond to forms of integrin β4. In F, the higher molecular weight band is likely laminin α5 and the lower doublet β1 and γ1. (E) The immunoblot shown in C was stripped and reprobed with anti-β1 integrin. No significant differences between samples can be seen. β1, mature β1 integrin; β1p, precursor β1.