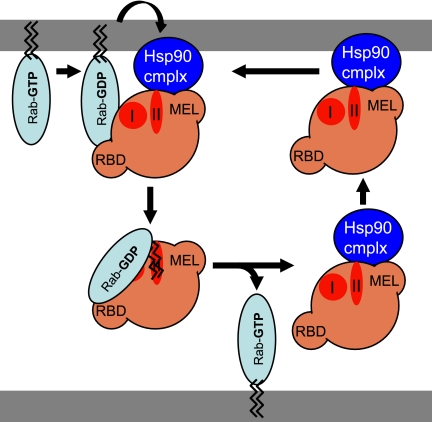
Figure 8.
Model for the role of Hsp90 in GDI-dependent Rab recycling pathways. Shown is a model describing the potential role of Hsp90 in GDI-dependent Rab recycling. Hsp90 and its cochaperone machinery are proposed to facilitate the recruitment of GDI to the membrane through MEL, configuring GDI in the domain II open configuration. After hydrolysis of Rab (GTP) to form Rab (GDP), GDI binds the Rab effector domain through domain I. This facilitates transfer of GG lipids from the lipid bilayer to the domain II GG binding pocket, resulting in release of the GDI–Rab (GDP) complex into the cytosol and dissociation from Hsp90. Discussion for details.