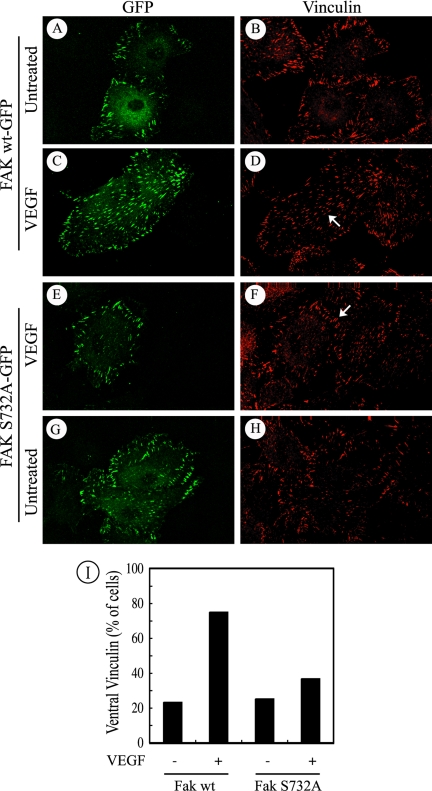
Figure 4.
Phosphorylation FAK on Ser732 is necessary for recruitment of vinculin in response to VEGF. Quiescent HUVECs transiently expressing wild-type FAK fused to GFP-tag or mutant FAK-Ser732Ala fused to GFP-tag were plated on gelatin-coated Lab-Tek chambers and left untreated (A and B, G and H) or were exposed to 5 ng/ml VEGF for 5 min (C–F). After treatments, cells were fixed, permeabilized, and costained for GFP detection (A, C, E, and G) using an anti-GFP antibody and then an anti-rabbit IgG-fluorescein isothiocyanate-conjugated antibody for detection in confocal fluorescence microscopy. Vinculin (B, D, F, and H) was detected using specific antibody coupled with a biotin-labeled anti-mouse IgG and revealed with Texas Red-conjugated streptavidin. Representative fields from two separate experiments are shown. The arrow in D denotes the recruitment of vinculin to the ventral focal adhesions in cells transfected with wild-type FAK and treated with 5 ng/ml VEGF. The arrow in F shows that, even in the presence of VEGF, vinculin remains at the periphery of the cells expressing the Ser732Ala mutant. (I) Quantification of cells showing recruitment of vinculin to the ventral focal adhesions. Quantification has been done on 400–500 cells for each condition.