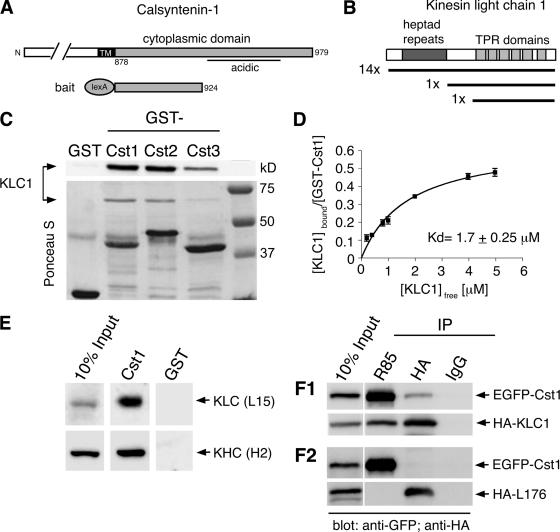
Figure 1.
The cytoplasmic segment of calsyntenin-1 binds directly to the light chain of Kinesin-1. (A) Schematic diagram illustrating the calsyntenin-1 bait construct (aa 878-924) used for the yeast two-hybrid screen. (B) Domain structure of KLC1. The regions encoding the 16 KLC1 cDNA clones isolated from the screen are depicted. (C) Recombinant KLC1 (15 μg) was incubated with beads coated with 5 μg GST or GST-calsyntenin fusion proteins (GST-Cst1, GST-Cst2, GST-Cst3). Bound proteins were analyzed by immunoblotting using an antibody against KLC1 (L15; top panel) and Ponceau-S staining of the membrane (bottom panel). All three calsyntenins interact with KLC1. (D) Estimation of the apparent binding affinity of calsyntenin-1 to KLC1. Increasing concentrations of KLC1 (0.2–5 μM) were incubated with 46 nM GST-Cst1. Bound and free KLC1 were measured, and the Kd was determined by curve-fitting as described in Materials and Methods (R2 = 0.95, n = 3). (E) Immobilized GST-Cst1 or GST (50 μg) was incubated with mouse brain extract. Bound proteins were analyzed by immunoblotting using the indicated antibodies. GST-Cst1 pulled down both KLC1 and KHC. (F1 and F2) HeLa cells were cotransfected with EGFP-calsyntenin-1 and HA-KLC1 (F1) or the KLC1 deletion construct HA-L176 (F2) followed by immunoprecipitations using the indicated antibodies. Immunoprecipitates were analyzed by immunoblotting with the indicated antibodies. EGFP-calsyntenin-1 coimmunoprecipitated with HA-KLC1, but not with HA-L176.