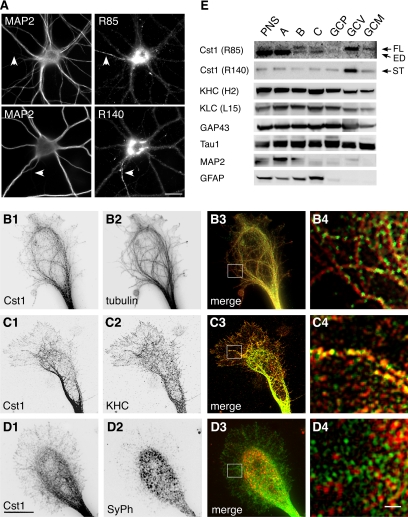
Figure 5.
Calsyntenin-1 colocalizes with Kinesin-1 in growth cones and is enriched in axonal growth cone vesicles. (A) Immunocytochemistry of cultured cortical neurons (14 DIV) using antibodies R85 or R140. Dendrites and axons (arrowheads) were discriminated by costaining with MAP2. Anti-calsyntenin-1 antibodies labeled tubulovesicular structures in the soma, in dendrites, and in the axon. Note the abundance of calsyntenin-1 immunoreactivity in the perinuclear region and in the axon. Scale bar, 30 μm. (B–D) Double stainings of axonal growth cones (4 DIV) with antibody R85 (B1–D1) and either tubulin (B2), KHC (C2), or synaptophysin (SyPh; D2). Note the alignment of calsyntenin-1–positive vesicles along microtubules (B3 and B4) and the partial colocalization with KHC (C3 and C4), but not with synaptophysin (D3 and D4). B4 to D4 show higher magnifications of the boxed areas in B3 to D3. Scale bar, 10 μm in D1 and 1 μm in D4. (E) Axonal growth cones were isolated from P7 mouse brains by subcellular fractionation and analyzed by Western blotting using the indicated antibodies. Full-length (FL) calsyntenin-1 and the calsyntenin-1 stump (ST) were enriched in the GCV fraction, with trace amounts present in the GCM fraction. Note the presence of KLC and KHC in the GCV fraction. ED, ectodomain; PNS, postnuclear supernatant. (A) Growth cone particle-enriched fraction; (B) synaptic elements; (C) axonal shafts. GCP, pelleted growth cone particles; GCV, growth cone vesicles; GCM, growth cone membranes.