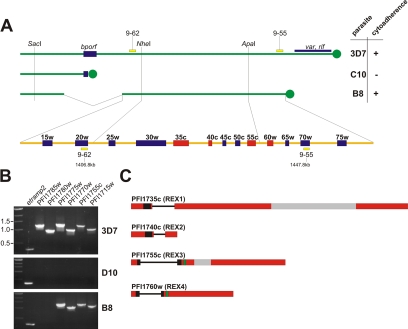
Figure 1.
Remapping of the region on the right arm of chromosome 9 linked to cytoadherence. (A) The right arm of chromosome 9 is shown for the P. falciparum isolates 3D7 (cytoadherent), C10 (noncytoadherent), and B8 (cytoadherent) (modified from Bourke et al., 1996). Single restriction sites determined by Southern analysis (Barnes et al., 1994) and the previously published markers 9-62 and 9-55 (Holt et al., 1998) were compared with the published 3D7 genome (www.PlasmoDB.org) using BLAST and virtual digests (NEBcutter, version 2.0; http://tools.neb.com/NEBcutter2/index.php). The region linked to cytoadherence and the predicted genes therein (as determined by the Plasmodium Sequencing Project and available at http://www.PlasmoDB.org) are indicated below (not drawn to scale). Genes PFI1715w–PFI1775w are indicated as 15w–75w. bporf, breakpoint open reading frame; telomeres are indicated as filled circles; the positions of the markers 9-62 and 9-55 on chromosome 9 are indicated in kilobase pairs; ring stage-specific genes are shown as red boxes. (B) PCR on genomic DNA of 3D7, D10 (which contains a deletion on the right arm of chromosome 9 similar to C10), and B8 showed that B8 still contains gene PFI1775w but not PFI1780w. Thus, the region linked to cytoadherence comprises the genes PFI1715w–PFI1775w. etramp2 was used as a positive control. (C) Gene structure of the four ring stage-specific genes in this region. Exons are indicated as boxes, introns as lines; hydrophobic stretches are indicated in black; PEXEL motifs in green; and areas encoding repeats are in gray.