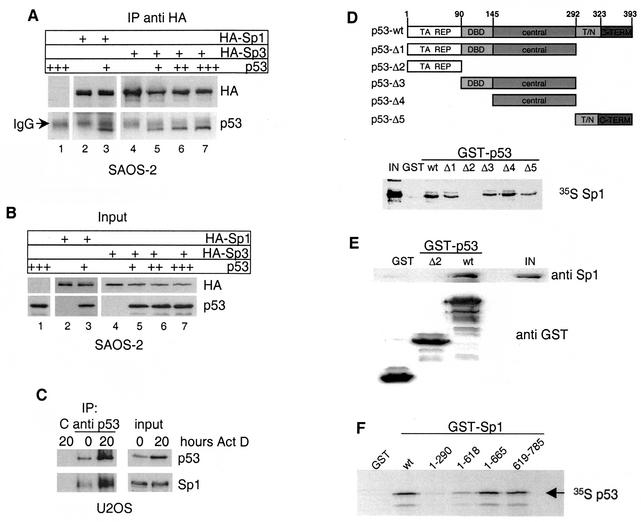
FIG. 4.
In vivo and in vitro interaction of p53 and Sp1-Sp3. (A) Western blot analysis of immunoprecipitates obtained with HA antibody from Saos-2 cells transfected with plasmids encoding either HA-Sp1 or HA-Sp3 alone or together with p53. The blot was subsequently probed with HA antibody to visualize Sp1 and Sp3 and p53 antibody to detect coimmunoprecipitated p53 protein. The signal from the cross-reaction with the heavy chain of HA antibody is indicated (IgG [immunoglobulin G]). IP, immunoprecipitation. (B) Western blot analysis of input protein levels of Sp1, Sp3, and p53. (C) U2OS cells were treated with 30 ng of actinomycin D/ml for 20 h, and p53 was immunoprecipitated before and after actinomycin D treatment. Immobilized 9E10 antibody was used as negative control (C). p53 and Sp1 were detected in immunoprecipitates and input extracts with the respective antibodies. IP, immunoprecipitation. (D) Upper panel: schematic representation of p53 deletion mutants used for GST pull-down experiments. Specific domains are labeled as follows: TA, transactivation; REP, repression; DBD, specific DNA-binding domain; central, central domain; T/N, tetramerization, nuclear localization; C-TERM, C terminus. Lower panel: GST pull-down assay done with the different GST-p53 constructs and in vitro-translated [35S]methionine-labeled Sp1. One hundred percent Sp1 protein input (IN) is shown as control. (E) GST pull-down assay with the indicated GST-p53 fusion constructs and purified Sp1 protein. p53-associated Sp1 and 20% of the input (IN) were detected by Western blot analysis. GST proteins were stained with Coomassie blue. (F) GST pull-down assay with the indicated GST-Sp1 constructs and in vitro-translated [35S]methionine-labeled human p53.