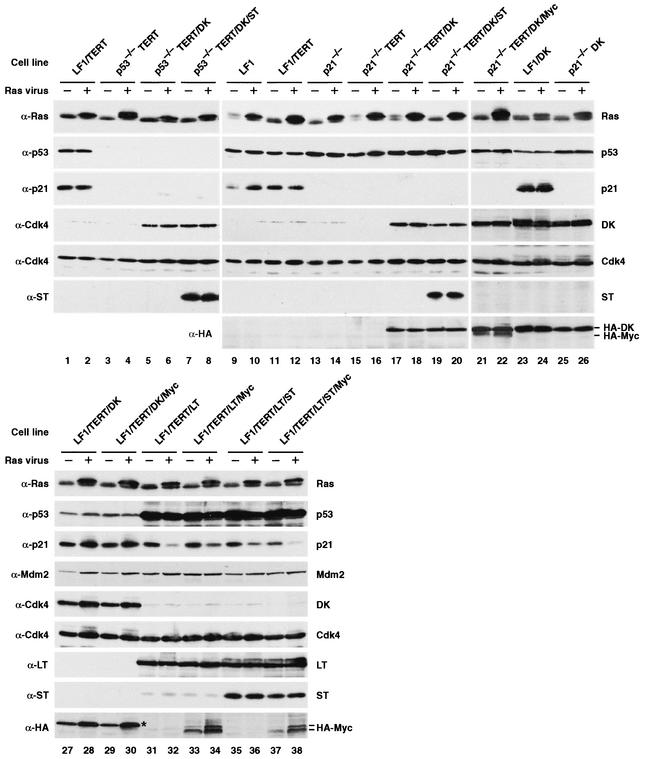
FIG. 3.
Immunoblot analysis of Ras-infected pools of cells. Exponentially growing cultures were infected with pBabe-mEYFP/Ras or empty pBabe-mEYFP vectors. Cultures were not subjected to selection with any drugs and were kept in the exponential growth phase by subculturing as needed. Six days after infection, four 10-cm-diameter dishes were harvested, pooled, and processed for immunoblotting. The cell line is indicated above each pair of lanes, and the virus used to infect the cells is indicated above each lane as follows: −, empty vector; +, Ras vector. The antibodies used (anti-Ras [α-Ras], etc.) are indicated to the left of the gels. The proteins detected are indicated to the right of the gels. DK, which has a HA tag, can be detected with both anti-Cdk4 and anti-HA antibodies. HA-tagged Myc (HA-Myc) was detected with anti-HA antibody and migrates as a doublet (lanes 33, 34, 37, and 38). The upper band of this doublet comigrates with the DK protein, which is also detected by the HA antibody (lanes 21 and 22). Note the relatively low expression of Myc in the LF1/TERT/DK/Myc cell line (lanes 29 and 30) (the position of the DK protein is marked by an asterisk), whereas the Myc protein is easily seen in the p21−/−TERT/DK/Myc cell line (lanes 21 and 22).