Figure 1.
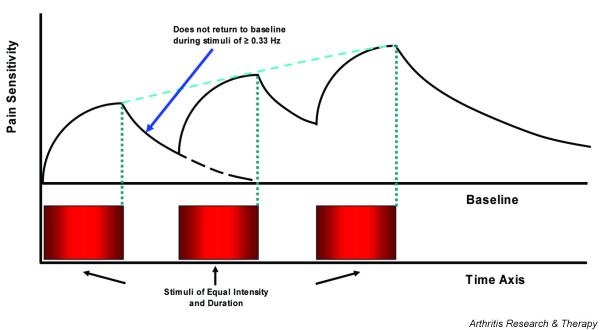
Temporal summation of second pain (windup). When identical stimuli are applied to normal subjects at frequencies of ≥0.33 Hz, pain sensations will not return to baseline during the interstimulatory interval. Windup is strongly dependent on stimulus frequency and is inversely correlated with interstimulatory interval [75]. In contrast to normal subjects, FM patients windup at frequencies of < 0.33 Hz and require lower stimulus intensities [40].
