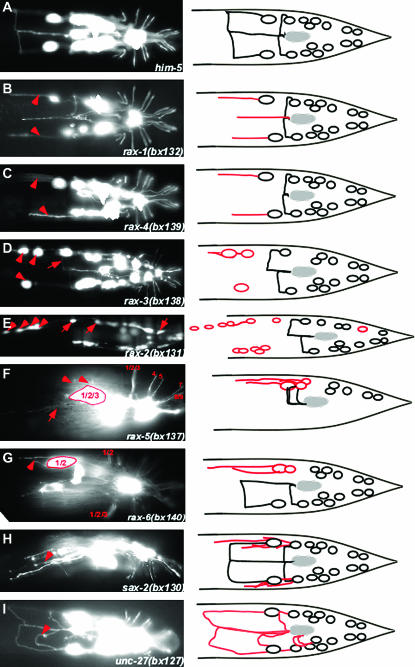
Figure 2.—
Abnormal ray neuron axon trajectories in mutants. Fluorescence photomicrographs and diagrams of wild-type and mutant axon trajectories. RnB neurons are labeled with pkd-2∷GFP (bxIs14). All diagrams and most photomicrographs are ventral views, whereas in the photomicrographs rax-5(bx137) is shown in ventrolateral view and sax-2(bx130) is shown in lateral view. Arrowheads and arrows point out specific defects as follows: (B and C) R1B axons fail to turn to the ventral side. (D) Abnormal anterior positions of R1B and R2B cell bodies and commissural pathway of R3B following the normal path of R1B (arrow). (E) Ectopic anterior GFP-positive cells and anterior displacement of R1B, R2B, and R8B cell bodies (arrows). (F) Despite abnormal clustering of their cell bodies, R1B, R2B, and R3B have normal commissures and also send out ectopic neurites that do not turn (arrow). (G) Ray 1 and 2 are fused; R1B and R2B cell bodies are clustered and send out axons that fail to turn. (H) Ray neurons extend multiple neurites. (I) Axons appear to take wandering pathways.