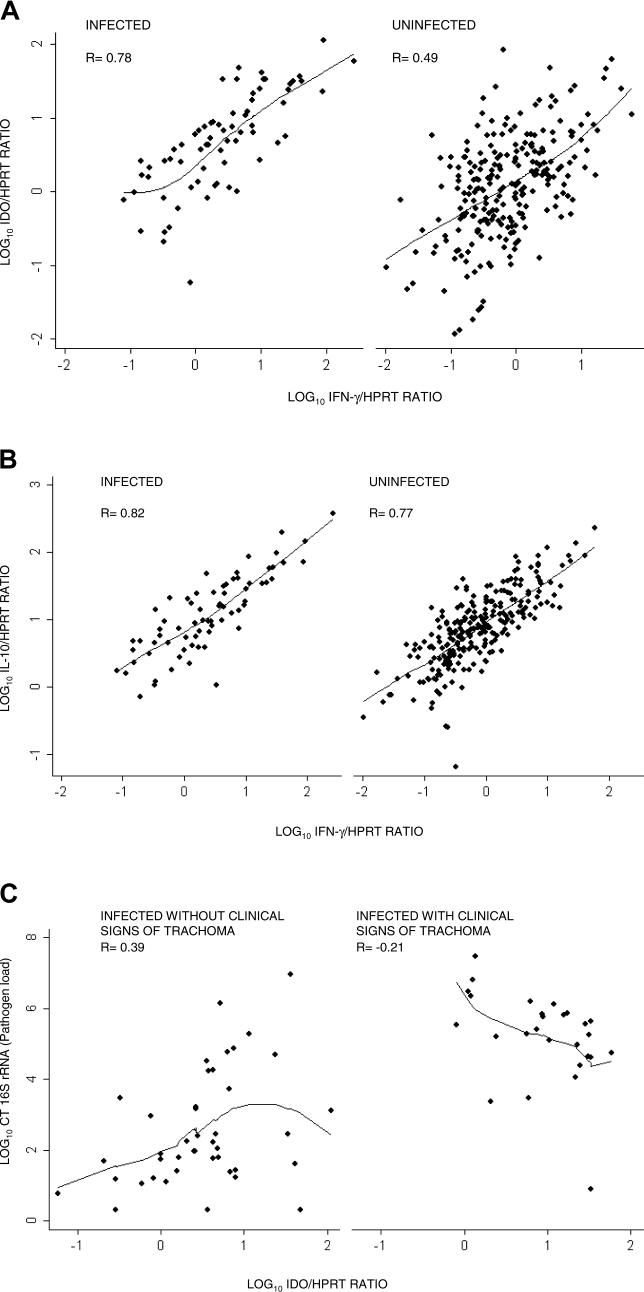
Figure 3. Correlations between Right Eye Conjunctival Gene Transcript Levels Reveal Linked Cytokine Responses and the Relationship to Control of Pathogen Load.
Abundance of IFN-γ, IL-10, and IDO relative to HPRT expression after log10 transformation. Correlation coefficients were calculated by Spearman's rank correlation and trend lines fitted by locally weighted polynomial regression.
(A) Strong positive correlation between the conjunctival expression of IDO and IFN-γ in individuals with infection (n = 69) or without infection (n = 238).
(B) Strong positive correlation between the expression of IFN-γ and counter inflammatory IL-10 in infected (n = 69) and uninfected individuals (n = 238).
(C) Relative abundance of IDO and the load of pathogen (chlamydial 16S rRNA) in the conjunctiva. A weak positive correlation was found between pathogen load and IDO expression in clinically normal individuals (n = 42) (mean pathogen loads are lower in this group; Table 2). In contrast, the relationship between IDO expression and pathogen load is weakly negative or absent in individuals with co-incident clinical signs of trachoma (n = 29) (pathogen loads are highest in this group; Table 2).
CT, C. trachomatis.