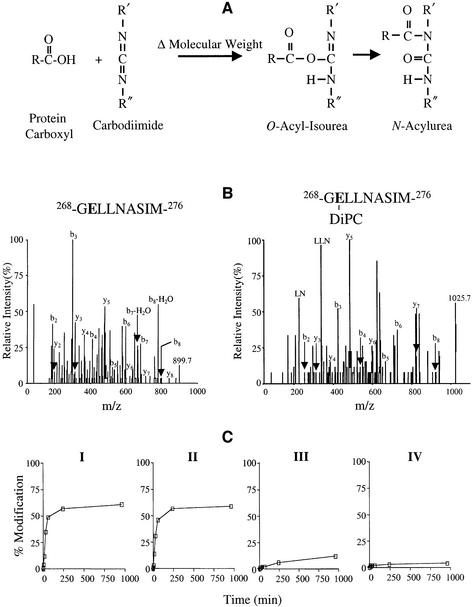
Fig. 4. Modification of Glu269 by carbodiimides. (A) Reaction of carbodiimide with carboxyl side-chain. Nucleophilic attack of a carbodiimide on a protonated carboxyl side-chain leads to the formation of O-acyl-isourea with a change in molecular weight (Δ molecular weight) followed by rearrangement to form an N-acylurea with no further change in mass. (B) Collision-induced dissociation spectrum of 268-GELLNASIM-276 and 268-GELLNASIM-276 modified with DiPC. Annotated peaks in the spectra include the singly charged parents (m/z 899.7 and 1025.7, respectively) and the b- and y-ion series. (C) Time course of 268-GELLNASIM-276 modification by carbodiimides with different solubilities. Purified LacY (∼20 µM) in DDM at pH 6.0 was incubated with 20 mM of the following carbodiimides at 30°C leading to the mass shifts shown in parentheses: DiPC (Δ126), DCCD (Δ206), CMC (Δ251) and EDC (Δ155). The total ion current from peptide 268-GELLNASIM-276 modified by carbodiimide divided by the total ion current from unmodified and modified 268-GELLNASIM-276 was used to calculate the percentage modification of Glu269. No measurable difference in the ionization efficiency of the unmodified and modified peptides was detected. Each point represents the average of two independent experiments. Maximum peak height in the absence of modification was ∼5 × 105 counts.

An official website of the United States government
Here's how you know
Official websites use .gov
A
.gov website belongs to an official
government organization in the United States.
Secure .gov websites use HTTPS
A lock (
) or https:// means you've safely
connected to the .gov website. Share sensitive
information only on official, secure websites.