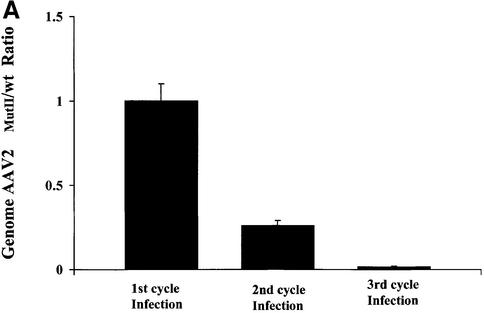
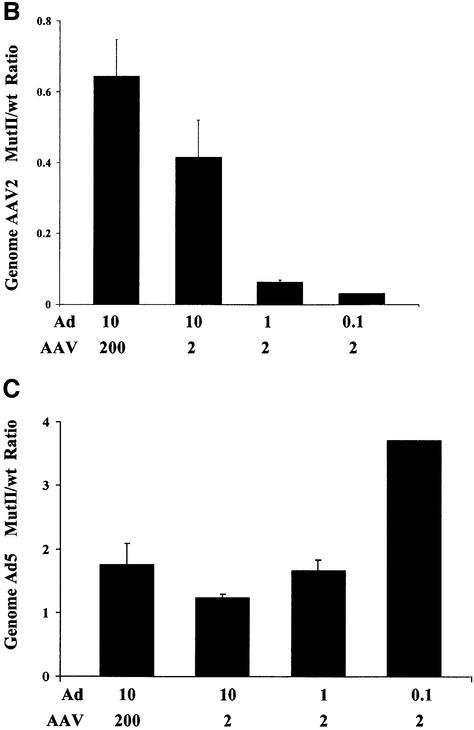
Fig. 7. Replication properties of AAV2MutII during repeated infection cycles and at different m.o.i. combinations. (A) HeLa cells were co- infected with AAV2wt/Ad or AAV2MutII/Ad with 50 particles/cell for each virus. Forty-eight hours post-infection wt and mutant AAV2 genomes were quantified by Q-PCR (1st cycle infection). A 1:100 fold dilution of the crude cell lysate from the first cycle of infection was used to initiate the second cycle of HeLa cell infections. Forty-eight hours post-infection wt and mutant AAV2 genomes were again quantified (2nd cycle infection). This process was repeated again (3rd cycle infection). Data are presented as the ratio of AAV2MutII/AAV2wt genomes, and are the means ± SD of four experiments, each conducted in duplicate. (B and C) HeLa cells were infected with either AAV2wt or MutII at an m.o.i. of 200 or 2, together with Ad at an m.o.i. of 10, 1 or 0.1. Seventy-two hours post-infection AAV2 (B) or Ad (C) viral DNA was quantified by Q-PCR. The data are presented as a ratio (AAV2MutII/AAV2wt) of the AAV2 or Ad viral DNA detected in the corresponding co-infection. Means ± SD of two independent experiments, each conducted in duplicate, are shown.

An official website of the United States government
Here's how you know
Official websites use .gov
A
.gov website belongs to an official
government organization in the United States.
Secure .gov websites use HTTPS
A lock (
) or https:// means you've safely
connected to the .gov website. Share sensitive
information only on official, secure websites.