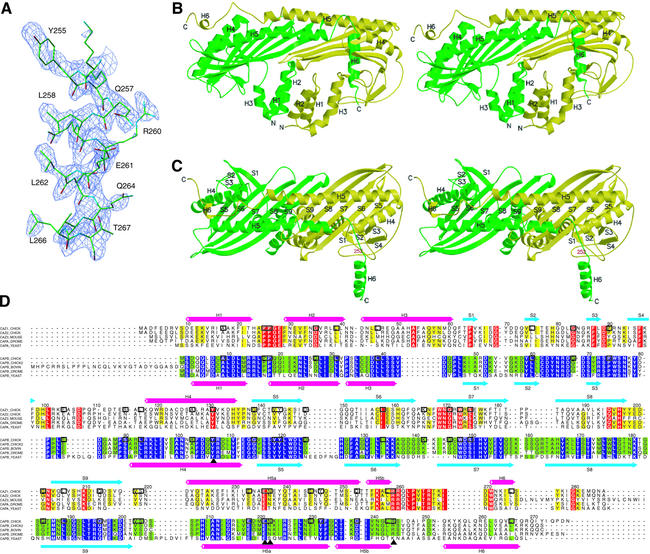
Fig. 1. Structure of the chicken CapZ α1β1 heterodimer. (A) The sigmaA-weighted Fo – Fc omit map with the refined structure of the C-terminal helix of the β subunit. The electron density map is contoured at 2.4 σ, and residues 252–271 are omitted for the phase calculation. (B and C) Stereo view of the ribbon representation of the CapZ crystal structure. The α and β subunits are shown in yellow and green, respectively. In (C), the molecule is viewed from the top side of that in (B), and residue 252 of the β subunit, the first residue of the disordered region in the Native 1 crystal, is indicated in red. (D) Sequence alignment of the proteins in the capping protein family. The sequences of chicken CapZ α1 (SWISS-PROT entry name CAZ1_CHICK) and β1 (CAPB_CHICK) are aligned based on their structures; those of chicken α2 (CAZ2_CHICK), mouse α3 (CAZ3_MOUSE), fruit fly α (CAPA_DROME) and yeast α (CAPA_YEAST) with chicken α1, and those of chicken β2 (alternative splice isoform of CAPB_CHICK, shown as CAPB_CHICK2 in the alignment), bovine β3 (CAPB_BOVINE), fruit fly β (CAPB_DROME) and yeast β (CAPB_YEAST) with chicken β1 are aligned with CLUSTAL W (Thompson et al., 1994). The residues conserved among ≥80% of the proteins of the same subunit, α or β, are indicated in yellow or green, and the strictly conserved residues are indicated in red or purple, respectively. The identical residues between chicken α1 and β1 are highlighted with boxes, and the important residues for stabilizing the structure described in the text are labeled with triangles. The secondary structures of chicken α1 and β1 are indicated above and below the sequences, respectively. The residue numbers for these two subunits are also shown.

An official website of the United States government
Here's how you know
Official websites use .gov
A
.gov website belongs to an official
government organization in the United States.
Secure .gov websites use HTTPS
A lock (
) or https:// means you've safely
connected to the .gov website. Share sensitive
information only on official, secure websites.