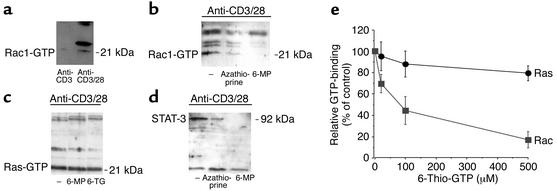
Figure 7.
(a) Rac1 activation assay in activated primary T cells. Purified CD4+ T lymphocytes were stimulated with IL-2 and antibodies to CD3 or IL-2 plus antibodies to CD3 and CD28 for 3 days. GTP-bound Rac1 (Rac1-GTP) was analyzed using PAK to determine Rac1 activation. CD28 costimulation led to induction of Rac1 activation in primary T cells. (b) Azathioprine and 6-MP suppress Rac1 activation. Purified CD4+ T lymphocytes were stimulated in the presence or absence of azathioprine or 6-MP for 3 days, as indicated. GTP-bound Rac1 was analyzed using PAK to determine Rac1 activation. Azathioprine treatment led to a reduction of CD28-dependent Rac1 activation. One representative experiment out of five is shown. (c) 6-MP and 6-TG fail to modulate Ras activation. GTP-bound Ras (Ras-GTP) was analyzed using Raf RGD to determine Ras activation. Azathioprine and its metabolites did not affect Ras activation. One representative experiment of three is shown. (d) Downregulation of STAT-3 in primary T cells upon treatment with azathioprine or 6-MP. Purified CD4+ T lymphocytes were stimulated in the presence or absence of azathioprine and 6-MP for 3 days, as indicated. Since Rac1 binds and activates STAT-3 (53), GTP-bound Rac1 was obtained using PAK, and STAT-3 levels were determined by immunoblotting. (e) Competition of GTP binding to Rac1 or Ras by 6-Thio-GTP. Recombinant Rac1 or Ras was incubated with radiolabeled GTP ([3H]GTP) and increasing amounts of chemically synthesized 6-Thio-GTP (0–500 μM). Next, Rac1 was obtained using PAK-1 agarose, followed by analysis of [3H]GTP-bound Rac1 by scintillation counting. Similarly, Ras was obtained using Raf RGD agarose followed by analysis of [3H]GTP-bound Ras by scintillation counting. 6-Thio-GTP led to a concentration-dependent suppression of [3H]GTP-bound Rac1 but had little effect on [3H]GTP-bound Ras.