Table 1.
Sedimentation equilibrium ultracentrifugation analysis of CzrA and NmtR
| Sample, 5 μM | Model | Molarmass, g/mol | Kdimer,×105 M−1* | χ2, ×10−5† |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| apo-CzrA‡ | Single, ideal¶ | 19307 | 4.66 | |
| Dissociable dimer‖ | 11975 | 1.7 (±0.3) | 4.59 | |
| Co(II)1-CzrA§ | Single, ideal | 20358 | 5.42 | |
| Dissociable dimer | 11851 | 4.8 (±0.1) | 5.56 | |
| Ni(II)1-CzrA§ | Single, ideal | 20126 | 4.71 | |
| Dissociable dimer | 12051 | 6.3 (±0.2) | 5.34 | |
| Zn(II)1-CzrA§ | Single, ideal | 19784 | 4.85 | |
| Dissociable dimer | 11858 | 4.5 (±0.2) | 5.21 | |
| apo-NmtR‡ | Single, ideal | 20069 | 4.57 | |
| Dissociable dimer | 12549 | 1.9 (±0.4) | 5.83 | |
| Co(II)1-NmtR§ | Single, ideal | 21952 | 5.96 | |
| Dissociable dimer | 12849 | 3.9 (±0.4) | 7.56 | |
| Ni(II)1-NmtR§ | Single, ideal | 21539 | 5.45 | |
| Dissociable dimer | 12877 | 4.1 (±0.4) | 6.22 | |
| Zn(II)1-NmtR§ | Single, ideal | 19359 | 5.41 | |
| Dissociable dimer | 12597 | 3.7 (±0.6) | 6.96 |
The association constant as estimated with a monomer–dimer equilibrium model (model 2).
x2 = (∑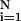 [f(Xi − Yi)]2/N − n), where N is the number of observations, n is the number of fitting parameters, f( ) is the fitting function, Xi and Yi are data points, and N − n equals the degrees of freedom.
[f(Xi − Yi)]2/N − n), where N is the number of observations, n is the number of fitting parameters, f( ) is the fitting function, Xi and Yi are data points, and N − n equals the degrees of freedom.
Conditions: 10 mM Hepes, 0.40 M NaCl, 0.1 mM EDTA, pH 7.0; 25°C.
Conditions: 10 mM Hepes, 0.40 M NaCl, pH 7.0; 25°C.
Model 1 fits the data to a single, ideal species with calculated dimer molecular weights of 23,715 g/mol for CzrA and 25,409 g/mol for NmtR (see Materials and Methods).
Model 2 fits the data to a reversible associating system assuming a monomer-dimer equilibrium. The calculated monomer molar masses are 11,857 g/mol for CzrA and 12,704 g/mol for NmtR (see Materials and Methods).
