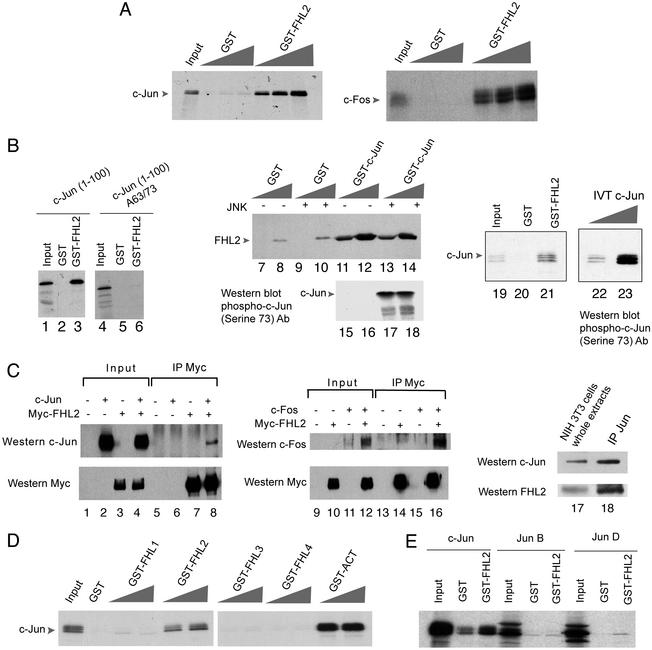
Figure 2.
FHL2 associates with AP-1. (A) FHL2 binds to c-Jun and c-Fos in vitro. GST pull-down assays were performed with in vitro translated radiolabeled c-Jun and c-Fos together with GST-FHL2 fusion protein. GST protein was used as a control. (B) For the interaction between c-Jun and FHL2, the c-Jun activation domain is sufficient, whereas the presence of Ser-63 and Ser-73 residues is necessary but their phosphorylation is not. GST pull-down experiments were performed by using GST-FHL2 together with in vitro translated c-Jun (1–100) and c-Jun (1–100) A63/A73. The binding between a GST-c-Jun protein, phosphorylated in vitro by JNK or not, and an in vitro translated FHL2 protein was assayed by GST pull-down. GST pull-down assay representing the interaction between GST-FHL2 and in vitro translated c-Jun was reproduced in parallel with a Western blot analysis by using a anti-phospho-c-Jun (Ser 73) antibody, to distinguish the binding of each phosphorylated form of c-Jun to GST-FHL2 protein. (C) FHL2 interacts with c-Jun and c-Fos in vivo. FHL2 coimmunoprecipitates with c-Jun and c-Fos, after cotransfection in mammalian cells of c-Jun, c-Fos, and Myc-FHL2 expression vectors (lanes 1–16). Immunoprecipitation was performed with the anti-Myc antibody. Whole extracts (Left) and immunocomplexes (Right) were analyzed by Western blot by using anti-c-Jun, anti-c-Fos, and anti-Myc antibodies. Endogenous FHL2 and c-Jun proteins from serum-stimulated NIH 3T3 cells coimmunoprecipitate (lanes 17–18). Immunoprecipitation was performed with an anti-c-Jun antibody and immunocomplexes were analyzed by Western blot with anti-c-Jun and anti-FHL2 antibodies. (D) GST pull-down assays show that in vitro translated c-Jun does not bind to GST-FHL1, GST-FHL3, GST-FHL4 proteins, but binds to GST-ACT protein. (E) GST pull-down experiments show that FHL2 is not interacting with other members of the Jun family, JunB and JunD. Equivalent amounts of the three Jun proteins were used.