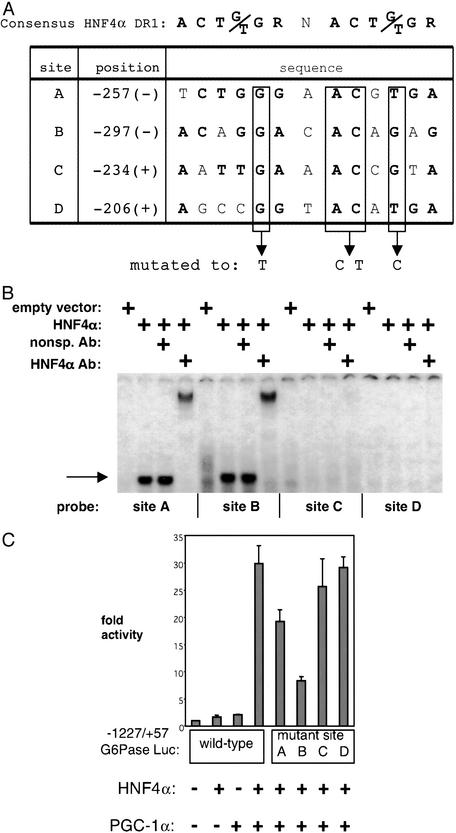
Figure 4.
Identification of HNF4α-binding sites in the G6Pase promoter. (A) Computer algorithm search for HNF4α-binding sites. The four highest-scoring potential HNF4α-binding sites (DR1s) between −298 and −180 of the G6Pase promoter are depicted with their position and sequence. The nucleotides in bold correspond to the consensus HNF4α-binding site. Boxed nucleotides were mutated within the context of the parent promoter construct. (B) HNF4α protein binds in vitro to sites A and B. Electrophoretic mobility-shift assays were conducted in which in vitro-translated HNF4α was incubated with radiolabeled probes corresponding to the sites depicted in A. The single arrow marks the level of the HNF4α-specific complex. A slower migrating complex is visible after the addition of an antibody against HNF4α. Free probe was in excess and is not shown. (C) Mutation of site B, and to a lesser extent of site A, impairs PGC-1α coactivation of HNF4α on the G6Pase promoter. Sites A–D on the G6Pase promoter were mutated as depicted in A. SV40-transformed hepatocytes were cotransfected with HNF4α and PGC-1α in the presence of these mutant reporters. The graph is representative of three independent trials.