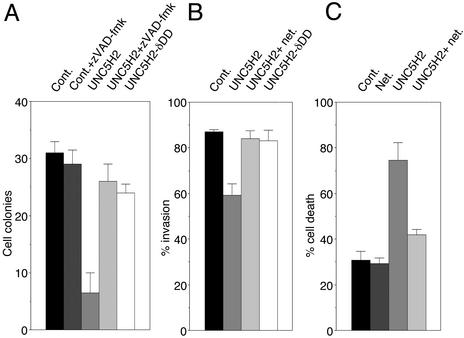
Figure 7.
UNC5H expression suppresses anchorage-independent growth and invasion in vitro by inducing apoptosis. (A) 293T cells were transfected with a mock plasmid or expressing constructs for UNC5H2 full-length or UNC5H2 deleted for its death domain (UNC5H2-δDD) and were assessed for growth in soft agar as in Fig. 5. To assay the role of apoptosis in the blockade of anchorage-independent growth by full-length UNC5H2, 20 μM zVAD-fmk was added repeatedly. (B) Similar experiment as in A but LS174T cells were assessed for invasion ability in Matrigel chambers for 2 days. As in Fig. 5 the filters were fixed and stained by using the Diff-Quick procedure (Dade Behring). Standard deviations are indicated (n = 3). (C) UNC5H2 induces cell death. Similar experiment as in A was performed except after 48 h of growth in soft agar, cells were stained with trypan blue and numerated as described (11). The percentage of cell death was obtained as ratio between the number of trypan blue-positive cells and the total number of cells. Standard deviations are indicated (n = 3).