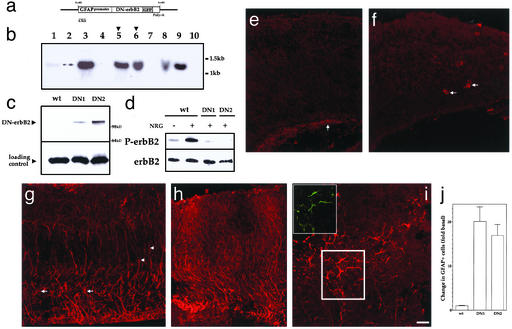
Figure 5.
Down-regulation of erbB2 function transforms radial glia into astrocytes in vivo. (a) The construct used for the generation of GFAP promoter-DNerbB2-GFP transgenic mice. (b) Southern blot analysis of founder mice. Of the seven founder lines, two (arrowhead) were used to establish breeding lines named DN1 and DN2. (c) DNerbB2-GFP transgene is expressed in the E16 cortices of DN1 and DN2 mice, but not in nontransgenic mice. DNerbB2-GFP protein expression was detected with anti-GFP antibodies. (d) NRG-1-induced tyrosine phosphorylation of erbB2 receptors is attenuated in E16 cortical cells from DN1 and DN2 mice. (Upper) Tyrosine phosphorylation of erbB2. (Lower) ErbB2 protein. (e–g) Minimal expression of GFAP-positive astrocytes in WT (E16) cortex. Arrows point to astrocytes found in association with blood vessels (f) or in the ventricular zone (e). (h–j) Increased number of GFAP+ astroglia were seen in DN1 (h) and DN2 (i and j) cortices. (Inset) DNerbB2-GFP transgene is expressed in astroglial cells. Transformed astrocytes in cortex (red) also label with anti-GFP antibodies (green). (k) An ≈17- to 20-fold increase in GFAP+ cells was found in DN1 and DN2 cerebral wall. Number of GFAP+ cells was counted in 10 sections of the cerebral wall from four embryos each of WT, DN1, and DN2. (Scale bar = e–g, 45 μm; h–j, 60 μm.)