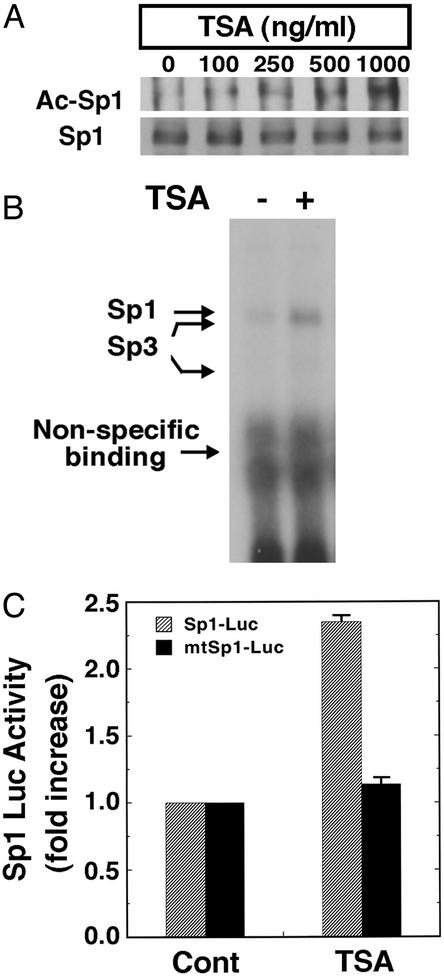
Figure 2.
HDAC inhibitors augment Sp1 acetylation, Sp1 DNA binding activity, and Sp1-dependent reporter gene expression in cortical neuronal cultures. (A) Sp1 acetylation levels in cortical neurons treated with the prototypic HDAC inhibitor TSA as determined by immunoprecipitation with an Sp1 Ab followed by immunoblotting with acetyl lysine Ab (Ac-Sp1) or Sp1 Ab alone (Sp1). Note that levels of Sp1 do not change with increasing concentrations of TSA. (B) TSA enhances binding of Sp1 and Sp3 to a canonical Sp1 DNA binding site. The electrophoretic mobility-shift assay was performed by using nuclear extracts from cortical neurons treated with and without TSA (100 ng/ml) for 60 min. The presence of Sp1 and Sp3 in each of the induced complexes was verified by supershift analysis. During this short period of TSA exposure, Sp1 or Sp3 protein levels did not change. (C) Sp1-dependent luciferase activity in control and TSA (100 ng/ml)-treated cortical neurons (gray bars). Note that luciferase activity does not change in the presence of TSA when the Sp1 response element has been mutated (black bars).