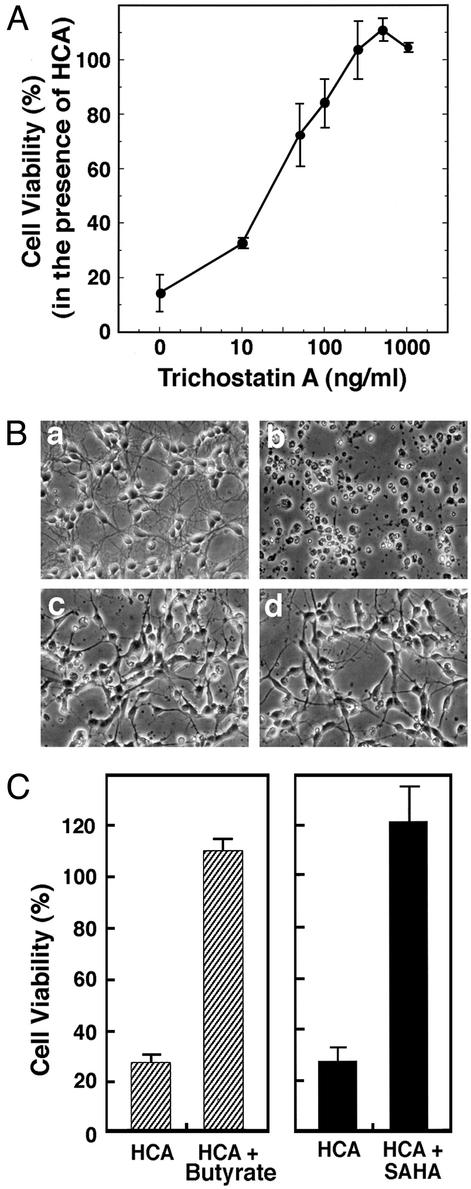
Figure 3.
HDAC inhibitors inhibit neuronal death induced by glutathione-depletion-induced oxidative stress. (A) TSA inhibits HCA-induced apoptosis in a concentration-dependent manner. Cell viability was measured by 3-(4,5-dimethylthiazol-2-yl)-2,5-diphenyl tetrazolium bromide (MTT) reduction. Lactate dehydrogenase (LDH) release assay and TUNEL were performed in parallel to verify that MTT changes reflect changes in viability. Each point is the mean ± SD of three to five independent experiments. (B) Phase-contrast microscopy of cortical neurons: (a) control; (b) 1 mM HCA; (c) 100 ng/ml TSA (note the change in the morphology of the cell bodies); and (d) 100 ng/ml TSA plus 1 mM HCA (note how TSA-treated neurons maintain their cell body and neurite morphology in the presence of 1 mM HCA). (Magnifications: ×200.) (C) Structurally distinct HDAC inhibitors, butyrate (5 mM) and SAHA (5 μM), also inhibit HCA-induced death. Cell viability was measured by using the MTT reduction, LDH release, or TUNEL as described in Experimental Methods. All methods gave quantitatively similar results.