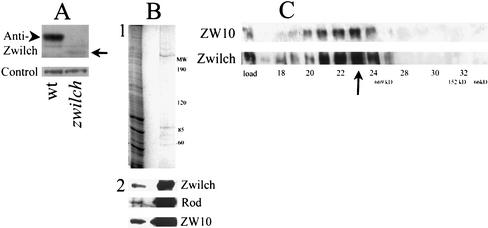
Figure 5.
Zwilch protein. (A) Anti-Zwilch antibody identifies Zwilch on a Western blot of third instar larvae from wild-type and from zwilch mutants (top). A 70-kDa band in wild-type (arrowhead) is replaced by much lower levels by a 60-kDa product in the mutant (arrow). The amount of protein in each lane was assayed with an unrelated antibody (bottom). (B) Zwilch is purified on the anti-ZW10 column. (1) Coomassie Blue staining of total embryonic extract (left lane) and a low pH elution from the column (right lane). (2) Western blot of the same gel probed with anti-Zwilch, anti-ROD, and anti-ZW10. (C) Zwilch and ZW10 cofractionate on a Superose 6 sizing column. Equal volumes of each fraction were analyzed on a Western blot probed with anti-Zwilch (bottom). The blot was then reprobed with anti-ZW10. A sample of the total extract is indicated in the load lane. The arrow indicates the peak fraction for both Zwilch and ZW10. The void volume was at fraction 13, and the salt front in fraction 42. Standards: 669 kDa, thyroglobulin; 66 kDa, bovine serum albumin; 158 kDa, aldolase.