Figure 1.
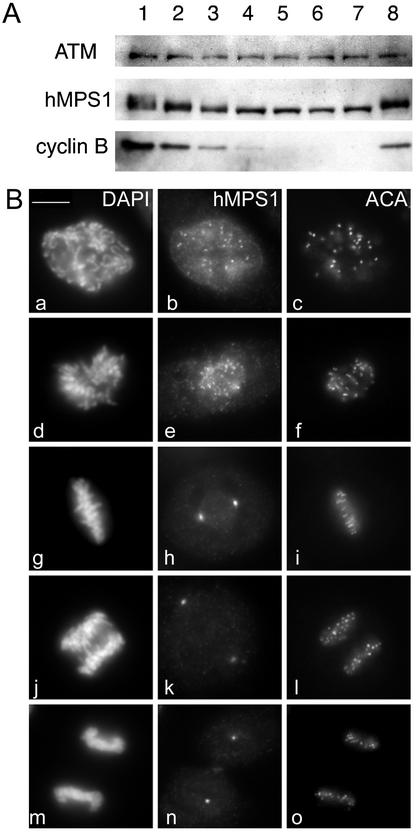
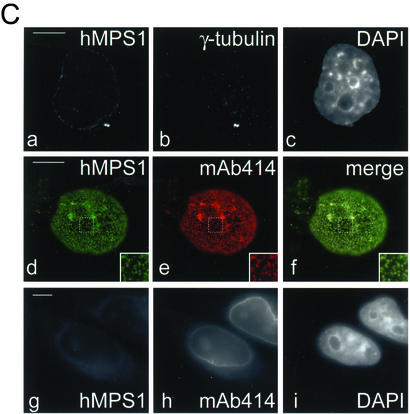
Mitotic phosphorylation and subcellular distribution of hMPS1. (A) hMPS1 is dephosphorylated when cells exit mitosis. HeLa cells that were blocked in mitosis with nocodazole were collected and released into drug-free medium, and samples were taken every 30 min up to 3 h (lanes 1–7; lane 1 is time 0). One sample was released into medium containing the proteosome inhibitor ALLN and harvested 3 h later (lane 8). Equal amounts of protein obtained from the different lysates were probed for hMPS1, cyclin B, and ATM. ATM was used as a loading control because its level has been shown to not fluctuate during the cell cycle (Gately et al., 1998). (B) Affinity-purified rabbit anti-hMPS1 antibodies were used to stain HeLa cells at various stages of mitosis: prophase (a–c), prometaphase (d–f), metaphase (g–i), anaphase (j–l), and telophase (m–o). DAPI and ACA (anticentromere autoimmune serum) were used to stain chromosomes and kinetochores, respectively. Note the bright foci of centrosome staining at spindle poles. (C) hMPS1 is localized to centrosomes and nuclear pores during interphase. Interphase HeLa cells were costained with rabbit anti-hMPS1 and mouse anti-γ tubulin (a–c) to verify hMPS1 at centrosomes. The presence of hMPS1 at nuclear pores was revealed by costaining with mAb414 (d and e). A merged image shows coincident localization of hMPS1 with mAb414 (f). Cells permeabilized with digitonin were stained with hMPS1 and mAb414 antibodies (g–i). Rabbit anti-hMPS1 was visualized with Alexafluor 488 anti-rabbit secondary antibodies. Mouse anti-γ-tubulin and mAb414 were visualized with Texas Red anti-mouse secondary antibodies. DNA was stained with DAPI. Bar, 10 μm.