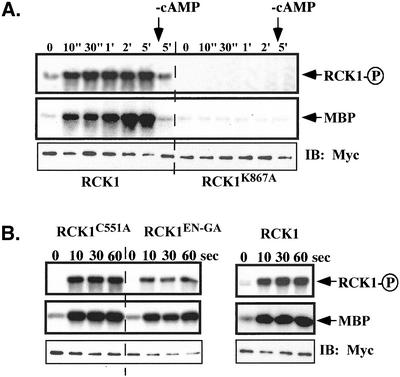
Figure 7.
Activation of RCK1 by cAMP stimulation. Aggregation-competent cells made by pulsing (see MATERIALS AND METHODS) were stimulated with cAMP and aliquots were taken at the time points indicated. Cells were lysed, RCK1 or its mutant was immunoprecipated with anti-myc monoclonal antibody, and kinase activity was measured as described in MATERIALS AND METHODS. (A) RCK1 kinase activity using MBP as a substrate before (0") and after stimulation (10"-5′). The kinase-dead mutant RCK1 K867A was used as a control and no activation was observed in these cells. To test the activity of RCK1 after the removal of cAMP, a sample was taken at the 1-min time point and 0.05 unit of PDE (phosphodiesterase; Sigma-Aldrich) was added. Cells were quickly washed twice with 12 mM Na+/K+ phosphate buffer and lysed at 5 min after addition of cAMP. The RCK1 kinase activity was assayed in the same experiment (marked −cAMP). Top, autophosphorylated RCK1. Middle, RCK1-phosphorylated MBP. To examine the immunoprecipitated RCK1 protein level, a Western blot was carried out on the same blot used for the kinase assay (bottom). (B) Kinase assay on RCK1 with mutations in the RGS domain including C551A and EN510-511GA. Top, autophosphorylated RCK1. Middle, RCK1-phosphorylated MBP. Bottom, immunoprecipitated RCK1 protein level. Wild-type RCK1 was used as a control.