FIG. 4.
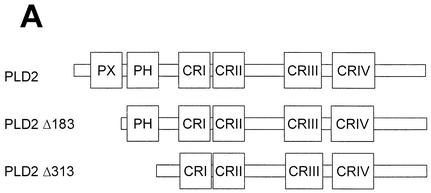
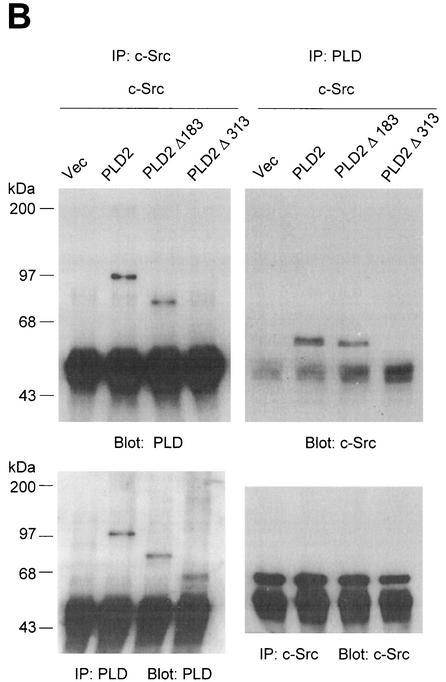
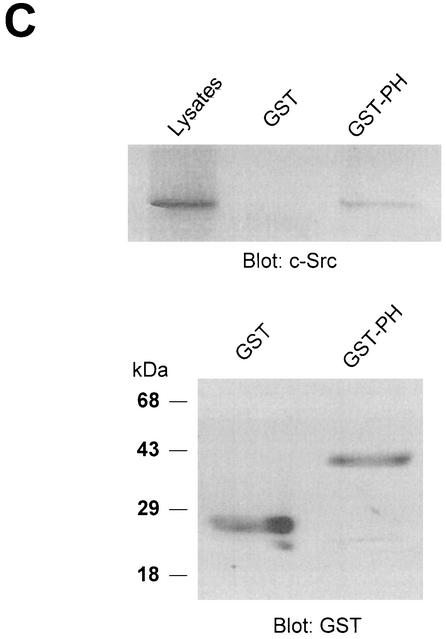
The N-terminal PH domain of PLD2 is required for interaction with c-Src. (A) Schematic representation of PLD2. The boxes indicate highly conserved sequences of PLD; their possible functions have been proposed or demonstrated in reference 52. CR, conserved region. (B) COS-7 cells were transiently cotransfected with plasmids encoding the empty vector (Vec) and c-Src, or PLD2 and c-Src, or N-terminal 183-amino-acid-truncated PLD2 Δ183(184-933) and c-Src, or N-terminal 313-amino-acid-truncated PLD2 Δ313(314-933) and c-Src. Cell lysates were subjected to immunoprecipitation by using anti-PLD or anti-c-Src antibodies, and the amount of coimmunoprecipitated c-Src or PLD was determined by immunoblotting with anti-c-Src or anti-PLD antibodies. Expression of PLD2 and c-Src was determined by using anti-PLD or anti-c-Src antibodies. (C) For the GST pull-down assay, GST-PH fusion protein was used as described in reference 29. The lysates transfected with c-Src were incubated with 2 μg of GST or GST-PH fragment and immunoblotted with antibody to c-Src. The amount of the GST fusion proteins was visualized by immunoblotting with an anti-GST antibody. Data are representative of three experiments.