FIG. 8.
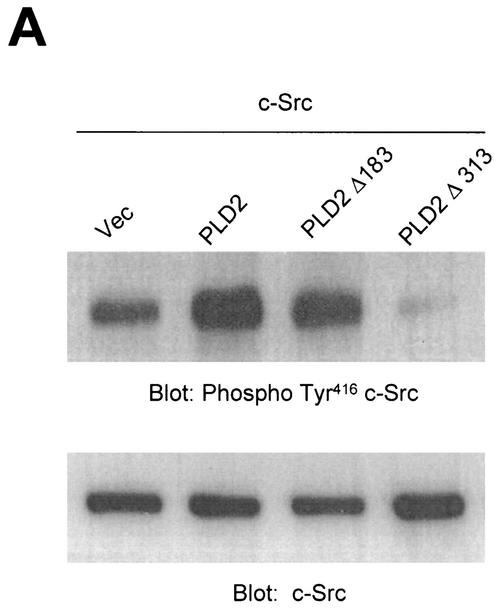
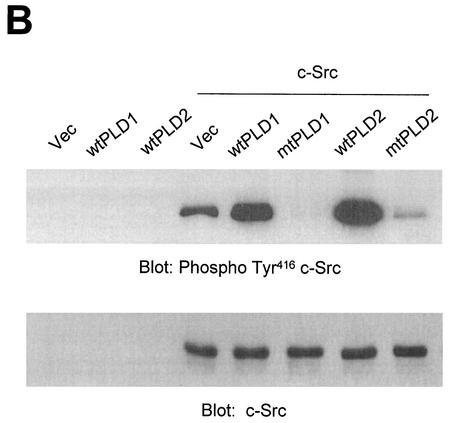
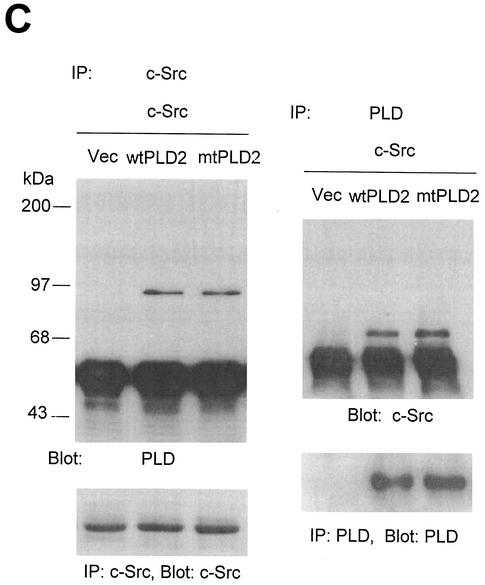
Overexpression of PLD stimulates c-Src kinase activity. (A) COS-7 cells were transiently cotransfected with various combinations of plasmids encoding empty vector (Vec) and c-Src, or PLD2 and c-Src, or N-terminal 183-amino-acid-truncated PLD2 Δ183(184-933) and c-Src, or N-terminal 313-amino-acid-truncated PLD2 Δ313(314-933) and c-Src. Cell lysates were subjected to immunoblot analysis using a phospho Tyr416 c-Src antibody. Expression of c-Src was determined by using an anti-c-Src antibody. (B) COS-7 cells were transiently transfected for 40 h with various combinations of plasmids encoding an empty vector, PLD1, PLD2, c-Src, and c-Src plus either wild-type (wt) or catalytically inactive mutant (mt) PLD1 or PLD2. Data are representative of three experiments. (C) COS-7 cells were transiently cotransfected with a catalytically inactive PLD2 mutant and wild-type c-Src, and cell lysates were subjected to immunoprecipitation with anti-c-Src antibody or anti-PLD antibodies. Immunoprecipitates were separated by SDS-PAGE and immunoblotted with anti-PLD or anti-c-Src antibody. Expression of PLD and c-Src was determined by using anti-PLD or anti-c-Src antibodies. Data are representative of three experiments.