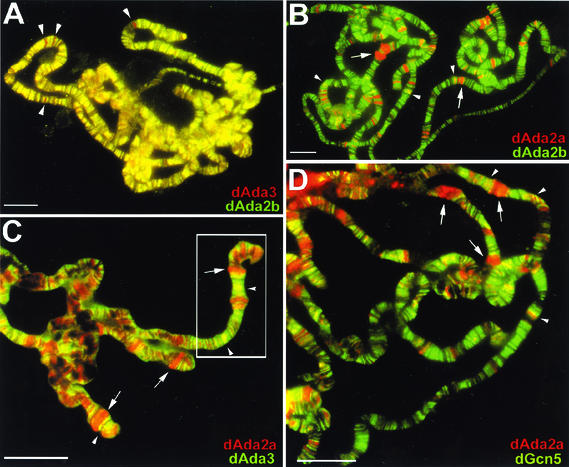
FIG. 7.
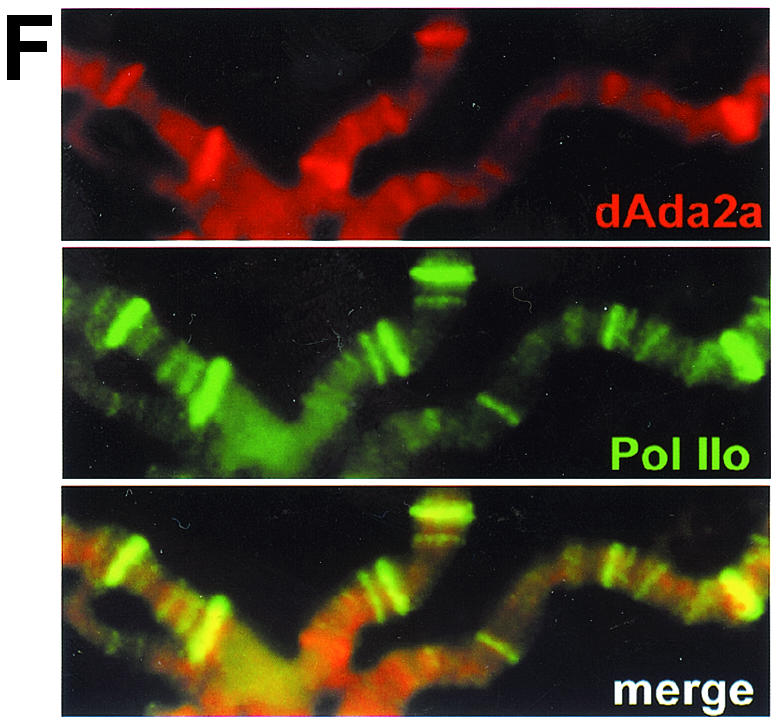
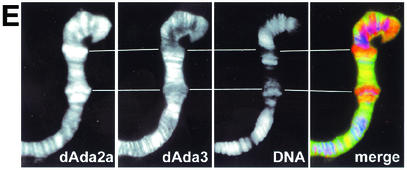
Localization studies of dAda2b and dAda2a on polytene chromosomes from third-instar larvae. Polytene chromosome spreads were double-labeled with the indicated affinity-purified antibodies. The pictures were taken at different magnifications; the bars correspond to 20 μm. (A to D) Merged red and green channels. (A) Costaining using rabbit anti-dAda3 antibodies (red) and rat anti-dAda2b antibodies (green). The arrowheads indicate selected regions exclusively staining for dAda3. (B) Costaining with rabbit anti-dAda2a (red) and rat anti-dAda2b (green). The arrowheads indicate selected regions of signal overlap. The arrows indicate puffs strongly staining for dAda2a. (C) Costaining with rat anti-dAda2a (red) and rabbit anti-dAda3 (green). The arrowheads indicate selected regions of signal overlap. The arrows indicate puffs strongly staining for dAda2a. (D) Costaining with rabbit anti-dAda2a (red) and rat anti-dGcn5 (green). The arrowheads indicate selected regions of overlap. The arrows indicate puffs strongly staining for dAda2a. (E) Magnification of the boxed region in panel C. DNA was stained with DAPI. dAda2a strongly stains decondensed euchromatic regions (compare the white bars). dAda3 and dAda2a colocalize in less condensed euchromatic regions. (F) dAda2a and phosphorylated RNA polymerase II colocalize on polytene chromosomes from third-instar larvae. Top, staining with rabbit anti-dAda2a antibodies; middle, staining with mouse anti-phosphorylated C-terminal domain of RNA polymerase II antibodies; bottom, overlap of green and red stains appears in the merge of panels A and B as yellow, yellow-green, and orange.