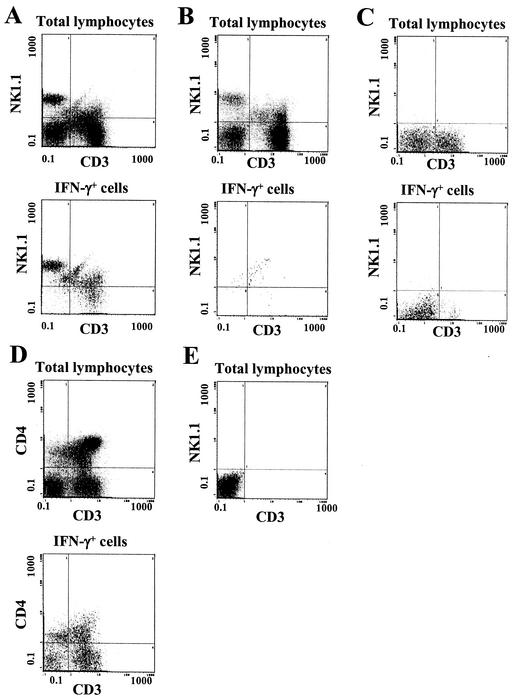
FIG. 3.
Phenotypes of hepatic lymphocytes that produce IFN-γ in response to E. coli challenge. Mice were injected i.p. with E. coli bacteria, and their hepatic lymphocytes were prepared 6 h later, treated with brefeldin A, and analyzed by flow cytometry. (A) Expression of CD3 and NK1.1 by various hepatic lymphocyte subsets of a representative E. coli-challenged B6 mouse. (Upper panel) Total hepatic lymphocytes after gating by light scatter; (lower panel) cells gated for the expression of intracellular IFN-γ. (B) Phenotypes of total or IFN-γ-expressing cells from a normal B6 mouse that had not been challenged with bacteria. (C) Analysis of the phenotypes of total and IFN-γ-expressing cells from a representative C3HeB/FeJ mouse, which lacks the NK1.1 allele. (D) Expression of CD3 and CD4 among total and IFN-γ-expressing hepatic lymphocytes of a representative B6 mouse. (E) Lack of staining of B6 hepatic lymphocytes in the absence of primary antibodies.