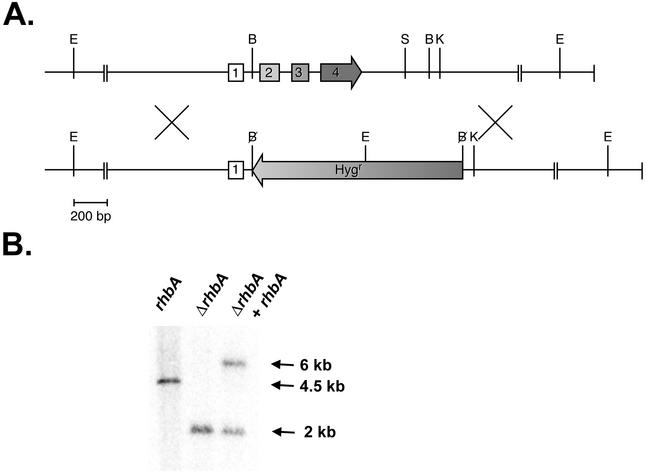
FIG. 1.
(A) Genomic organization of the rhbA gene (top) and the rhbA deletion construct (bottom). The rhbA deletion construct was built by replacing the BglII fragment of the rhbA genomic clone with the hygromycin resistance gene. The restriction sites include EcoRI (E), BglII (B), SacI (S), and KpnI (K) sites. Numbers indicate the four coding exons. (B) Southern blot of genomic DNA from the wild type (rhbA), the ΔrhbA strain (ΔrhbA), and the reconstituted strain (ΔrhbA + rhbA) cut with EcoRI and probed with an rhbA exon 1 probe. Homologous recombination of the deletion construct at the rhbA locus results in the introduction of an EcoRI site that reduces the size of the hybridizing band. Introduction of the complementation construct at a nonhomologous locus results in maintenance of the ΔrhbA band and the appearance of a larger band corresponding to the integrated complementation construct.