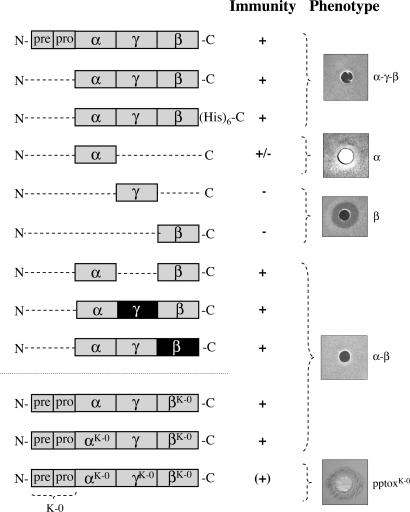
Fig. 2.
The α subunit of K28 is essential but not sufficient to confer protective immunity. Schematic drawing and effect on toxin immunity of K28 wild-type pptox and various truncated variants thereof lacking the N-terminal prepro sequence after in vivo expression in the K28-susceptible strain S. cerevisiae SEY6210. In the K1/K28 chimeric constructs, the corresponding subunits from K1 pptox are indicated by a black box. In each case, pptox expression was driven from the GAL1 promoter, and K28 immunity was determined in a well-plate assay on MBA (pH 4.7) with galactose as carbon source. In the pptox variants α/βK-0, αK-0/βK-0 and pptoxK-0, the single lysine residue in β or all internal lysyl residues in either both subunits or in the entire preprotoxin had been converted to arginine to reduce or prevent lysine-mediated α/β ubiquitination in vivo (see also Fig. 3G). The particular toxin construct producing the exemplarily shown halo on MBA is indicated in the figure. Note that toxin-treated cells of K28-α-expressing yeast show a small but cell-free zone of growth inhibition around the well, whereas pptoxK-0-expressing cells show a dark blue colony staining around the well, indicating that the cells are being killed by the toxin.