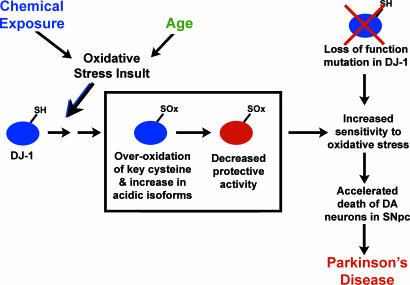
Fig. 6.
Model of DJ-1 loss of function by modification and mutation in Parkinson’s disease. Oxidative stress resulting from environmental exposure or aging leads to oxidation of DJ-1 (blue, active DJ-1) at key cysteine residues (SOx) and the inactivation of DJ-1 biological activity to protect against oxidative stress (red, inactive DJ-1). This is proposed to lead to increased sensitivity to oxidative stress, accelerated loss of dopaminergic (DA) neurons in the substantia nigra pars compacta (SNpc) and contribute to the development of sporadic Parkinson’s disease. In inherited parkinsonism due to loss of DJ-1 gene (top right), cells have increased sensitivity to oxidative stress from initial stages, leading to accelerated loss of dopaminergic neurons and Parkinson’s disease.