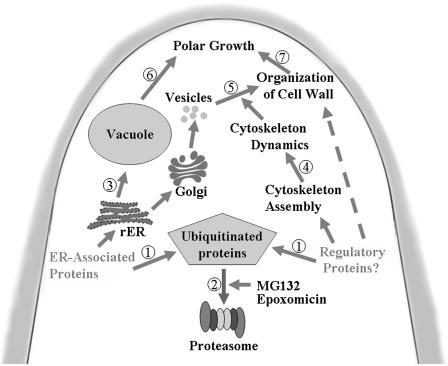
Figure 13.
Hypothetical model summarizing effects of proteasome inhibitors on the tip growth of P. wilsonii pollen tubes. Part of ER-associated proteins and regulatory proteins essential for cytoskeleton assembly are ubiquitinated (1) and then degraded by 26S proteasome (2) during pollen tube growth. Inhibition of proteasome activity promotes accumulation of UbPs, which causes ER-derived vacuolization (3) and disruption of cytoskeleton (4) in pollen tubes. Consequently, reduction of vesicle trafficking (5) results in the disorganization of cell wall. Simultaneous vacuolization (6) and weakening of cell wall (7) lead to the disruption of tip growth, accompanied by irregularly broadened tube diameter and/or swollen tip.