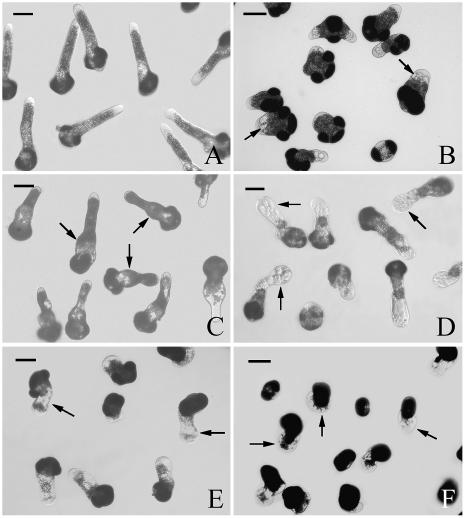
Figure 2.
Effects of MG132 on P. wilsonii tube morphology. A, Pollen tubes cultured under control conditions for 24 h, showing normal length and shape. B, Pollen tubes treated with 40 μm MG132 for 20 h, showing the formation of vacuoles at the subapical region of the tube (arrows). C, Pollen tubes treated with 40 μm MG132 for 20 h, then MG132 was washed out, and tubes were cultured in fresh medium without inhibitor for additional 8 h. Note that tubes could recover their growth with normal morphology except obviously broadened base of tubes from previous treatment. D, Pollen tubes treated with 40 μm MG132 for 24 h, showing the inhibitor-induced cellular vacuolization, tip swelling (arrows), and irregularly broadened diameter. E, Pollen tubes treated with 2 μm epoxomicin for 24 h, arrows indicate the inhibitor-induced cellular vacuolization, tip swelling, and irregularly broadened diameter. F, Pollen tubes treated with 4 μm epoxomicin for 24 h, arrows show the serious effects on tube morphology and severe growth inhibition. Bars = 50 μm.