Abstract
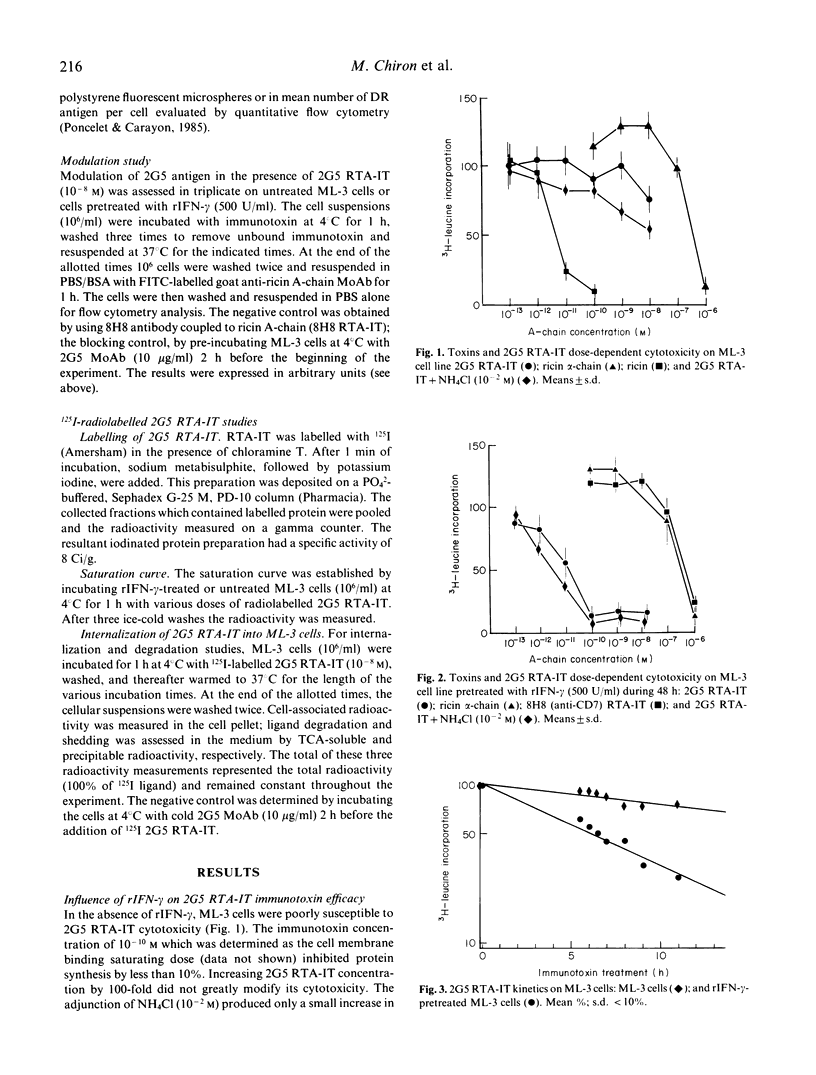
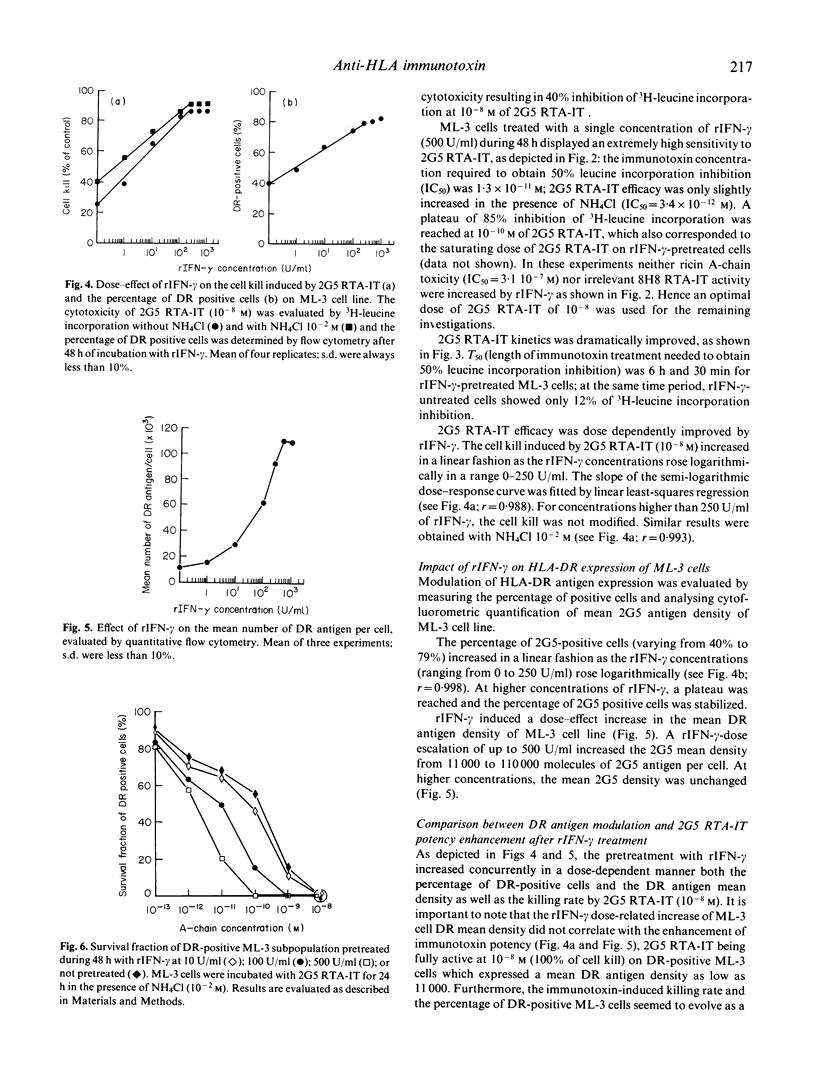
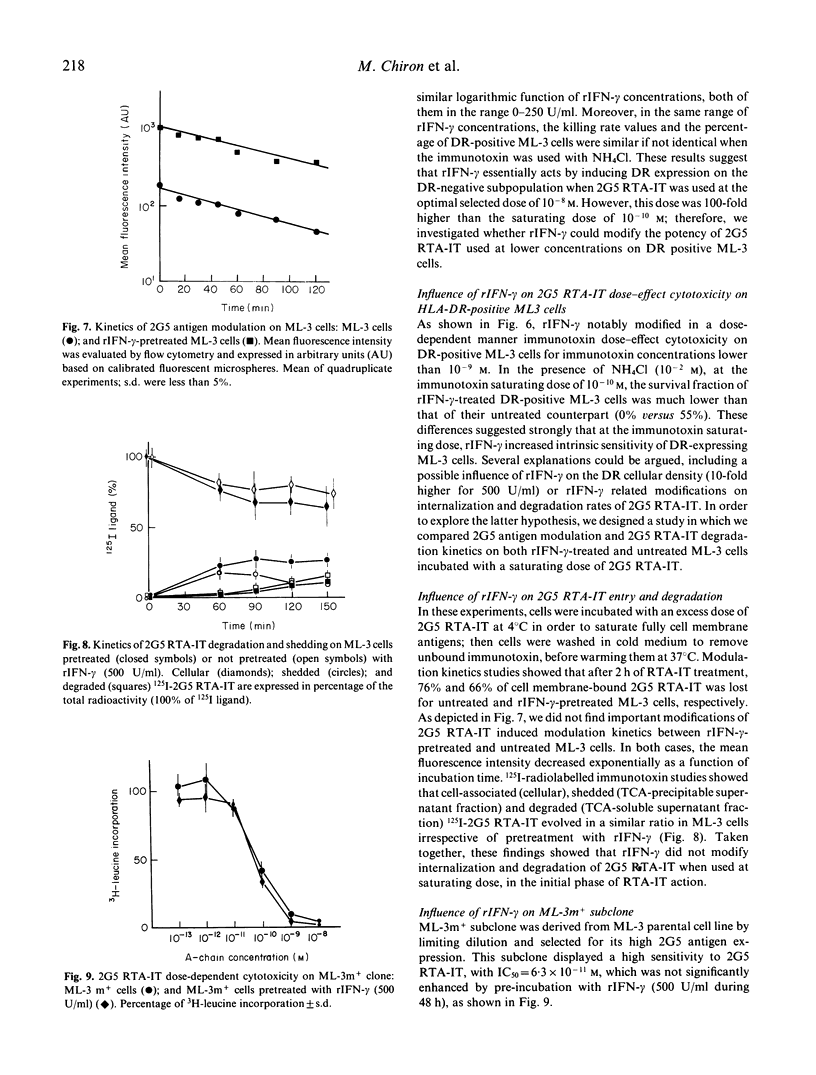
In order to evaluate the impact of induction and increase target antigen expression on immunotoxin potency, we measured the potentiating effect of recombinant immune interferon-gamma (rIFN-gamma) on the cytotoxicity of an anti HLA-DR ricin A-chain immunotoxin (2G5 RTA-IT) on the myeloid cell line ML-3. After 48 h of incubation with rIFN-gamma (500 U/ml) the percentage of 2G5-positive cells increased from 40% to 79%, and the 2G5 mean density was enhanced by 10-fold (11,000 versus 110,000 molecules/cell). Concurrently, rIFN-gamma pretreatment induced a dramatic improvement of 2G5 RTA-IT dose-effect cytotoxicity, as well as immunotoxin cytotoxicity kinetics. When 2G5 RTA-IT was used at the optimal dose of 10(-8)M (the maximum dose which avoided non-specific ricin A-chain cytotoxicity), the immunotoxin-induced cell kill increased with the percentage of DR-positive ML-3 cells according to a similar linear-logarithmic function of rIFN-gamma concentration. Moreover, in the same range of rIFN-gamma concentrations, the killing values and the percentage of DR-positive ML-3 cells were similar if not identical. These findings imply that the enhancement of 2G5 RTA-IT cytotoxicity by rIFN-gamma is mainly related to the rIFN-gamma 2G5 antigen induction on HLA-DR negative cells when immunotoxin was used at 10(-8) M. Furthermore, 2G5 RTA-IT dose-effect cytotoxicity on DR-expressing ML-3 cells, when used at lower concentrations, was also increased by rIFN-gamma in a dose-dependent manner. This result suggests that for immunotoxin concentrations close to the limiting membrane saturation dose (10(-10)M), rIFN-gamma may not solely act by inducing HLA-DR expression on DR-negative ML-3 subpopulation but also by increasing individual cellular DR density on DR expressing ML-3 cells. Finally, our study showed that immunotoxin potency on malignant cell populations which display an heterogeneous antigen expression, could be greatly improved by the use of rIFN-gamma.
Full text
PDF



Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Amatruda T. T., 3rd, Bohman R., Ranyard J., Koeffler H. P. Pattern of expression of HLA-DR and HLA-DQ antigens and mRNA in myeloid differentiation. Blood. 1987 Apr;69(4):1225–1236. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Balkwill F. R., Stevens M. H., Griffin D. B., Thomas J. A., Bodmer J. G. Interferon gamma regulates HLA-D expression on solid tumors in vivo. Eur J Cancer Clin Oncol. 1987 Jan;23(1):101–106. doi: 10.1016/0277-5379(87)90426-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Borden E. C. Augmented tumor-associated antigen expression by interferons. J Natl Cancer Inst. 1988 Apr 6;80(3):148–149. doi: 10.1093/jnci/80.3.148. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carrel S., Schmidt-Kessen A., Giuffrè L. Recombinant interferon-gamma can induce the expression of HLA-DR and -DC on DR-negative melanoma cells and enhance the expression of HLA-ABC and tumor-associated antigens. Eur J Immunol. 1985 Feb;15(2):118–123. doi: 10.1002/eji.1830150204. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Casellas P., Bourrie B. J., Gros P., Jansen F. K. Kinetics of cytotoxicity induced by immunotoxins. Enhancement by lysosomotropic amines and carboxylic ionophores. J Biol Chem. 1984 Aug 10;259(15):9359–9364. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Casellas P., Canat X., Fauser A. A., Gros O., Laurent G., Poncelet P., Jansen F. K. Optimal elimination of leukemic T cells from human bone marrow with T101-ricin A-chain immunotoxin. Blood. 1985 Feb;65(2):289–297. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Demur C., Derocq J. M., Poncelet P., Chiron M., Roubinet F., Jaffrezou J. P., Bordier C., Laurent G. Effects of an anti HLA-DR immunotoxin on leukaemia cells and hematopoietic progenitors. Leuk Res. 1989;13(12):1047–1054. doi: 10.1016/0145-2126(89)90149-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Derocq J. M., Laurent G., Casellas P., Vidal H., Poncelet P., Fauser A., Demur C., Jansen F. Rationale for the selection of ricin A-chain anti-T immunotoxins for mature T cell depletion. Transplantation. 1987 Dec;44(6):763–769. doi: 10.1097/00007890-198712000-00008. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fellous M., Kamoun M., Gresser I., Bono R. Enhanced expression of HLA antigens and beta 2-microglobulin on interferon-treated human lymphoid cells. Eur J Immunol. 1979 Jun;9(6):446–449. doi: 10.1002/eji.1830090606. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ghosh A. K., Cerny T., Wagstaff J., Thatcher N., Moore M. Effect of in vivo administration of interferon gamma on expression of MHC products and tumour associated antigens in patients with metastatic melanoma. Eur J Cancer Clin Oncol. 1989 Nov;25(11):1637–1643. doi: 10.1016/0277-5379(89)90310-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Giacomini P., Aguzzi A., Pestka S., Fisher P. B., Ferrone S. Modulation by recombinant DNA leukocyte (alpha) and fibroblast (beta) interferons of the expression and shedding of HLA- and tumor-associated antigens by human melanoma cells. J Immunol. 1984 Sep;133(3):1649–1655. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Greiner J. W., Hand P. H., Noguchi P., Fisher P. B., Pestka S., Schlom J. Enhanced expression of surface tumor-associated antigens on human breast and colon tumor cells after recombinant human leukocyte alpha-interferon treatment. Cancer Res. 1984 Aug;44(8):3208–3214. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gros O., Gros P., Jansen F. K., Vidal H. Biochemical aspects of immunotoxin preparation. J Immunol Methods. 1985 Aug 2;81(2):283–297. doi: 10.1016/0022-1759(85)90213-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Herlyn M., Guerry D., Koprowski H. Recombinant gamma-interferon induces changes in expression and shedding of antigens associated with normal human melanocytes, nevus cells, and primary and metastatic melanoma cells. J Immunol. 1985 Jun;134(6):4226–4230. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laurent G., Kuhlein E., Casellas P., Canat X., Carayon P., Poncelet P., Correll S., Rigal F., Jansen F. K. Determination of sensitivity of fresh leukemia cells to immunotoxins. Cancer Res. 1986 May;46(5):2289–2294. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marth C., Fuith L. C., Böck G., Daxenbichler G., Dapunt O. Modulation of ovarian carcinoma tumor marker CA-125 by gamma-interferon. Cancer Res. 1989 Dec 1;49(23):6538–6542. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Matsui M., Nakanishi T., Noguchi T., Ferrone S. Synergistic in vitro and in vivo anti-tumor effect of daunomycin-anti-96-kDa melanoma-associated antigen monoclonal antibody CL 207 conjugate and recombinant IFN-gamma. J Immunol. 1988 Aug 15;141(4):1410–1417. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Piguet V., Carrel S., Diserens A. C., Mach J. P., de Tribolet N. Heterogeneity of the induction of HLA-DR expression by human immune interferon on glioma cell lines and their clones. J Natl Cancer Inst. 1986 Feb;76(2):223–228. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Poncelet P., Carayon P. Cytofluorometric quantification of cell-surface antigens by indirect immunofluorescence using monoclonal antibodies. J Immunol Methods. 1985 Dec 17;85(1):65–74. doi: 10.1016/0022-1759(85)90274-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Preijers F. W., Tax W. J., Wessels J. M., Capel P. J., De Witte T., Haanen C. Different susceptibilities of normal T cells and T cell lines to immunotoxins. Scand J Immunol. 1988 May;27(5):533–540. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-3083.1988.tb02380.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rowlinson G., Balkwill F., Snook D., Hooker G., Epenetos A. A. Enhancement by gamma-interferon of in vivo tumor radiolocalization by a monoclonal antibody against HLA-DR antigen. Cancer Res. 1986 Dec;46(12 Pt 1):6413–6417. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Taramelli D., Fossati G., Mazzocchi A., Delia D., Ferrone S., Parmiani G. Classes I and II HLA and melanoma-associated antigen expression and modulation on melanoma cells isolated from primary and metastatic lesions. Cancer Res. 1986 Jan;46(1):433–439. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Uckun F. M., Gajl-Peczalska K. J., Kersey J. H., Houston L. L., Vallera D. A. Use of a novel colony assay to evaluate the cytotoxicity of an immunotoxin containing pokeweed antiviral protein against blast progenitor cells freshly obtained from patients with common B-lineage acute lymphoblastic leukemia. J Exp Med. 1986 Feb 1;163(2):347–368. doi: 10.1084/jem.163.2.347. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


